Page 21 - SP015 Past Years PSPM Chapter 6 -14 Ver 2020
P. 21
PSPM SP015
PSPM JAN 1999/2000 SF025/2 No. 10(c)
28. A solid sphere and a ring shaped body having the same mass M and radius R are let to
roll in the same direction on a flat plane. Calculate the ratio of kinetic energy of the ring
to the kinetic energy of the solid sphere.
2
2
(Given moment of inertia of sphere = MR and moment of inertia of ring = MR )
2
5
[5 m]
PSPM JUN 1999/2000 SF025/2 No. 1
29. A cylindrical roller of mass 2.8 kg rotates with a speed of 1500 rotations per minute. If
the diameter of the cross-sectional area is 32.0 cm,
(a) calculate the angular momentum of the cylindrical roller. [3 m]
(b) determine the torque required to stop the cylindrical roller in 7.0 s. [1 m]
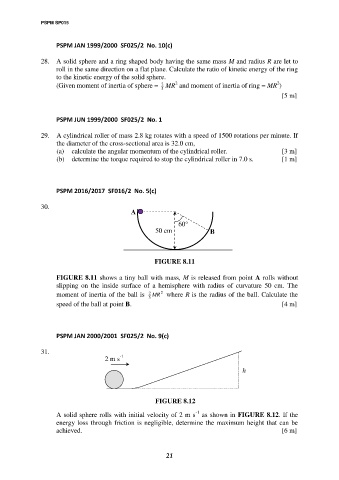
PSPM 2016/2017 SF016/2 No. 5(c)
30.
A
60
50 cm B
FIGURE 8.11
FIGURE 8.11 shows a tiny ball with mass, M is released from point A rolls without
slipping on the inside surface of a hemisphere with radius of curvature 50 cm. The
2
moment of inertia of the ball is MR where R is the radius of the ball. Calculate the
2
5
speed of the ball at point B. [4 m]
PSPM JAN 2000/2001 SF025/2 No. 9(c)
31.
2 m s -1
h
FIGURE 8.12
-1
A solid sphere rolls with initial velocity of 2 m s as shown in FIGURE 8.12. If the
energy loss through friction is negligible, determine the maximum height that can be
achieved. [6 m]
21