Page 215 - Account 10
P. 215
6. Rules for Debit and Credit
The New Accounting System of Government of Nepal is completely based on the
principle of double entry book-keeping system. Thus, the rules for debit and credit are
exactly the same as studied under the book keeping in the class nine. Here, the rules/
principles for debit and credit are discussed pointwise under two approaches.
i. Account approach
It classifies the heading which may be involved in various financial transactions, into
three accounts. The accounts, involved in the transactions, examples and the respective
rules/principles for debit and credit are discussed below:
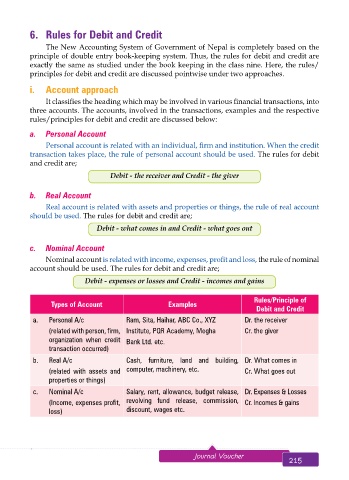
a. Personal Account
Personal account is related with an individual, firm and institution. When the credit
transaction takes place, the rule of personal account should be used. The rules for debit
and credit are;
Debit - the receiver and Credit - the giver
b. Real Account
Real account is related with assets and properties or things, the rule of real account
should be used. The rules for debit and credit are;
Debit - what comes in and Credit - what goes out
c. Nominal Account
Nominal account is related with income, expenses, profit and loss, the rule of nominal
account should be used. The rules for debit and credit are;
Debit - expenses or losses and Credit - incomes and gains
Rules/Principle of
Types of Account Examples
Debit and Credit
a. Personal A/c Ram, Sita, Haihar, ABC Co., XYZ Dr. the receiver
(related with person, firm, Institute, PQR Academy, Megha Cr. the giver
organization when credit Bank Ltd. etc.
transaction occurred)
b. Real A/c Cash, furniture, land and building, Dr. What comes in
(related with assets and computer, machinery, etc. Cr. What goes out
properties or things)
c. Nominal A/c Salary, rent, allowance, budget release, Dr. Expenses & Losses
(Income, expenses profit, revolving fund release, commission, Cr. Incomes & gains
loss) discount, wages etc.
214 Aakar’s Office Practice and Accountancy - 10 Journal Voucher 215