Page 463 - leadership-experience-2008
P. 463
CikguOnline
CikguOnline
444 PART 5: THE LEADER AS SOCIAL ARCHITECT
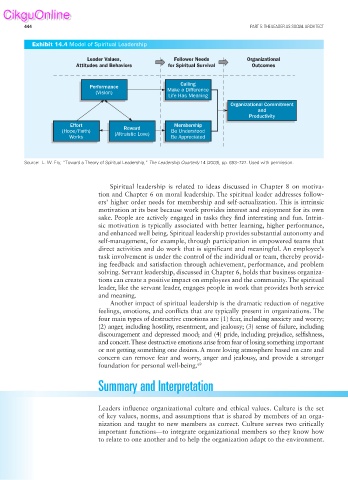
Exhibit 14.4 Model of Spiritual Leadership
Leader Values, Follower Needs Organizational
Attitudes and Behaviors for Spiritual Survival Outcomes
Calling
Performance
(Vision) Make a Difference
Life Has Meaning
Organizational Commitment
and
Productivity
Effort Reward Membership
(Hope/Faith) (Altruistic Love) Be Understood
Works Be Appreciated
Source: L. W. Fry, “Toward a Theory of Spiritual Leadership,” The Leadership Quarterly 14 (2003), pp. 693–727. Used with permission.
Spiritual leadership is related to ideas discussed in Chapter 8 on motiva-
tion and Chapter 6 on moral leadership. The spiritual leader addresses follow-
ers’ higher order needs for membership and self-actualization. This is intrinsic
motivation at its best because work provides interest and enjoyment for its own
sake. People are actively engaged in tasks they fi nd interesting and fun. Intrin-
sic motivation is typically associated with better learning, higher performance,
and enhanced well being. Spiritual leadership provides substantial autonomy and
self-management, for example, through participation in empowered teams that
direct activities and do work that is signifi cant and meaningful. An employee’s
task involvement is under the control of the individual or team, thereby provid-
ing feedback and satisfaction through achievement, performance, and problem
solving. Servant leadership, discussed in Chapter 6, holds that business organiza-
tions can create a positive impact on employees and the community. The spiritual
leader, like the servant leader, engages people in work that provides both service
and meaning.
Another impact of spiritual leadership is the dramatic reduction of negative
feelings, emotions, and conflicts that are typically present in organizations. The
four main types of destructive emotions are (1) fear, including anxiety and worry;
(2) anger, including hostility, resentment, and jealousy; (3) sense of failure, including
discouragement and depressed mood; and (4) pride, including prejudice, selfi shness,
and conceit. These destructive emotions arise from fear of losing something important
or not getting something one desires. A more loving atmosphere based on care and
concern can remove fear and worry, anger and jealousy, and provide a stronger
foundation for personal well-being. 69
Summary and Interpretation
Leaders infl uence organizational culture and ethical values. Culture is the set
of key values, norms, and assumptions that is shared by members of an orga-
nization and taught to new members as correct. Culture serves two critically
important functions—to integrate organizational members so they know how
to relate to one another and to help the organization adapt to the environment.