Page 662 - alligood 8th edition_Neat
P. 662
CHAPTER 32 Phil Barker 643
and relationships are described carefully, specifically, The Holistic Assessment, the person’s story, is at
and metaphorically, though not necessarily concisely. the heart of care planning and is represented as a
It is Barker’s terms like “problems in living,” mental heart. The circle of security assessment and plan sur-
distress, and view of people experiencing problems rounds the heart, all of which is surrounded by the
as “persons” that guide nurses to a proper focus. The interprofessional team circle (Figure 32–2).
identification of “human needs” rather than psycho- The continuum of care (immediate, transitional,
logical, social, or physical needs also provides clarity and developmental) intersects with the focus of care
and focus. How nurses see persons and how persons (Barker, 2000e; Barker & Buchanan-Barker, 2007a)
want to be nursed are clearly illustrated through (Figure 32–3).
the core category of “knowing you, knowing me.” Barker and Buchanan-Barker (2007a) provide a
Three subcategories, ordinary me, pseudo-ordinary or map or overview of the continuum of care or voyage
engineered-me, and professional me each have four of the person who enters, progresses through, and
dimensions: depth of knowing, power, time, and exits the service (Figure 32–4).
translation (Barker, Jackson, & Stevenson, 1999a; This easily understood theory is accessible concep-
Jackson & Stevenson, 2004). tually and linguistically through the use of everyday
In practice, using the person’s own language, rather language.
than jargon or professional language, contributes to
the theory’s success and its clarity. Major concepts of Simplicity
collaboration, empowerment, relationships, solution The Tidal Model is based upon a few simple ideas
focus, empowering through relationships, narrative, about “being human” and “helping one another”
and the use of “problems in living” are sufficiently (Barker, 2000e). It is comprehensive, elegant in its
clear and open the theory for use in other areas of simplicity, and at a level of abstraction to guide prac-
nursing and health care. tice, education, research, and policy. However, the
A number of concepts and relationships are pre- concepts themselves are complex, and the broad
sented elegantly and schematically within the Tidal relationships among the concepts add to the com-
Model. The person’s unique lived experience is synergis- plexity of the Tidal Model; people and relationships
tic and reciprocal among the World, Self, and Others, are inherently complex.
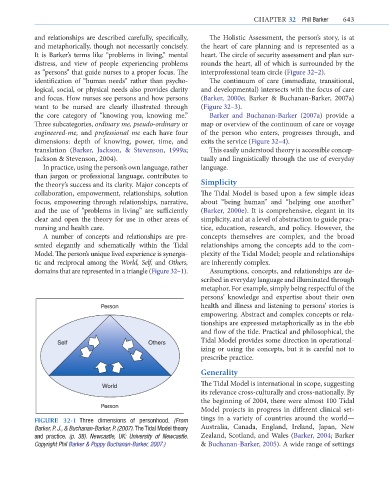
domains that are represented in a triangle (Figure 32–1). Assumptions, concepts, and relationships are de-
scribed in everyday language and illuminated through
metaphor. For example, simply being respectful of the
persons’ knowledge and expertise about their own
Person health and illness and listening to persons’ stories is
empowering. Abstract and complex concepts or rela-
tionships are expressed metaphorically as in the ebb
and flow of the tide. Practical and philosophical, the
Tidal Model provides some direction in operational-
Self Others
izing or using the concepts, but it is careful not to
prescribe practice.
Generality
The Tidal Model is international in scope, suggesting
World
its relevance cross-culturally and cross-nationally. By
the beginning of 2004, there were almost 100 Tidal
Person Model projects in progress in different clinical set-
FIGURE 32-1 Three dimensions of personhood. (From tings in a variety of countries around the world—
Barker, P. J., & Buchanan-Barker, P. (2007). The Tidal Model theory Australia, Canada, England, Ireland, Japan, New
and practice. (p. 38). Newcastle, UK: University of Newcastle. Zealand, Scotland, and Wales (Barker, 2004; Barker
Copyright Phil Barker & Poppy Buchanan-Barker, 2007.) & Buchanan-Barker, 2005). A wide range of settings