Page 664 - alligood 8th edition_Neat
P. 664
CHAPTER 32 Phil Barker 645
Enters service
Re-enters service
Developmental Orientation to Immediate Care
Care Plan
Exit
Transitional Holistic Security
Care Plan Assessment Assessment
Group work One-One Personal
1/2/3 Sessions Security
Planning
Immediate Care Plan
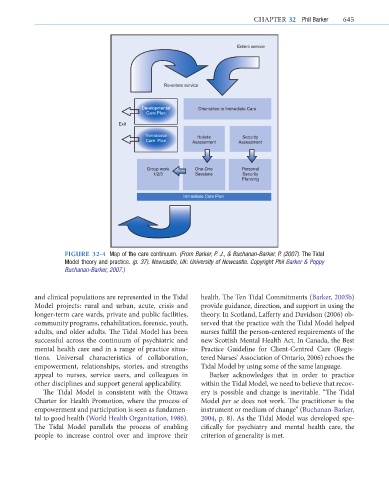
FIGURE 32-4 Map of the care continuum. (From Barker, P. J., & Buchanan-Barker, P. (2007). The Tidal
Model theory and practice. (p. 37). Newcastle, UK: University of Newcastle. Copyright Phil Barker & Poppy
Buchanan-Barker, 2007.)
and clinical populations are represented in the Tidal health. The Ten Tidal Commitments (Barker, 2003b)
Model projects: rural and urban, acute, crisis and provide guidance, direction, and support in using the
longer-term care wards, private and public facilities, theory. In Scotland, Lafferty and Davidson (2006) ob-
community programs, rehabilitation, forensic, youth, served that the practice with the Tidal Model helped
adults, and older adults. The Tidal Model has been nurses fulfill the person-centered requirements of the
successful across the continuum of psychiatric and new Scottish Mental Health Act. In Canada, the Best
mental health care and in a range of practice situa- Practice Guideline for Client-Centred Care (Regis-
tions. Universal characteristics of collaboration, tered Nurses’ Association of Ontario, 2006) echoes the
empowerment, relationships, stories, and strengths Tidal Model by using some of the same language.
appeal to nurses, service users, and colleagues in Barker acknowledges that in order to practice
other disciplines and support general applicability. within the Tidal Model, we need to believe that recov-
The Tidal Model is consistent with the Ottawa ery is possible and change is inevitable. “The Tidal
Charter for Health Promotion, where the process of Model per se does not work. The practitioner is the
empowerment and participation is seen as fundamen- instrument or medium of change” (Buchanan-Barker,
tal to good health (World Health Organization, 1986). 2004, p. 8). As the Tidal Model was developed spe-
The Tidal Model parallels the process of enabling cifically for psychiatry and mental health care, the
people to increase control over and improve their criterion of generality is met.