Page 5 - CH-1-(sample)
P. 5
Fastrack - 10
Web pages on the WWW are connected by links called hypertext links. Each hypertext link leads to
another Web page / Website. So, unlike reading a book where one page follows another in sequence, on
the World Wide Web you follow the web of links to visit the information you are interested in. This is
called Surfing.
THE WEB ADDRESSING SYSTEM
Each Web page (.html document) has its own address on the Internet, which is called a URL
or a Uniform Resource Locator through which it is identified and accessed on the Web server and
Web browser.
To recognize a web page, computers convert a URL like www.cbse.nic.in to numerical IP addresses
(like 200.200.200.165).
A URL is made up of the following parts:
http://www. organization name. top level domain suffix. Country name suffix
http - the communication protocol Top-level domain suffix
used to receive the document
Example: http://www.cbse.nic.in/welcome.htm
The orgainzation name The country name suffix Name of the .html document
Several top-level domains (TLDs) are common:
com Commercial enterprise mil U.S. Military entry
edu Educational institution net Network access provider
gov U.S. Government entity org Usually non-profit organizations
In addition, dozens of domain names have been assigned to identify and locate files stored on servers in
countries around the world. These are referred to as country codes.
Ch Switzerland Jp Japan
De Germany Uk United Kingdom
HOW DOES THE WWW WORK?
Have you ever wondered how exactly a Web page that you requested for finds its way into your
browser and onto your computer screen? The process is largely dependent on Web servers. Let us
understand how it works. Observe how a web page WWW reaches your computer
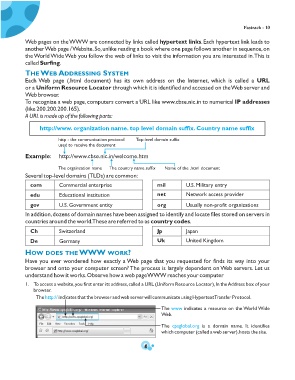
1. To access a website, you first enter its address, called a URL (Uniform Resource Locator), In the Address box of your
browser.
The http:// indicates that the browser and web server will communicate using Hypertext Transfer Protocol.
The www indicates a resource on the World Wide
Web.
The cpsglobal.org is a domain name. It identifies
which computer (called a web server), hosts the site.
4