Page 7 - Engineering Mathematics Workbook_Final
P. 7
Linear Algebra
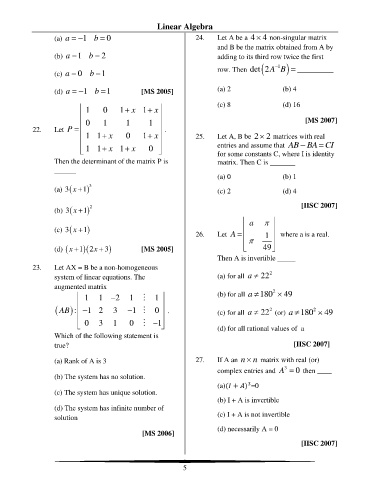
(a) a = − 1 b = 0 24. Let A be a 4 4 non-singular matrix
and B be the matrix obtained from A by
(b) a = 1 b = 2 adding to its third row twice the first
)
−
1
det
(c) a = 0 b = 1 row. Then (2A B = __________
(d) a = − 1 b = 1 [MS 2005] (a) 2 (b) 4
1 0 1 x 1 x (c) 8 (d) 16
+
+
0 1 1 1 [MS 2007]
22. Let P = .
+
+
1 1 x 0 1 x 25. Let A, B be 2 2 matrices with real
− =
1 1 x 1 x 0 entries and assume that AB BA CI
+
+
for some constants C, where I is identity
Then the determinant of the matrix P is matrix. Then C is _______
______
(a) 0 (b) 1
3
(a) ( 3 x + ) 1 (c) 2 (d) 4
2
(b) ( 3 x + ) 1 [IISC 2007]
a
(c) ( 3 x + ) 1
26. Let A = 1 where a is a real.
(d) ( x + 1 )(2x + ) 3 [MS 2005] 49
Then A is invertible _____
23. Let AX = B be a non-homogeneous
2
system of linear equations. The (a) for all a 22
augmented matrix
1 1 − 2 1 M 1 (b) for all a 180 2 49
( AB ): − 1 2 3 − 1 M 0 . (c) for all a 22 (or) a 180 2
2
49
0 3 1 0 M − 1
Which of the following statement is (d) for all rational values of a
true? [IISC 2007]
(a) Rank of A is 3 27. If A an n n matrix with real (or)
complex entries and A = 0 then ____
3
(b) The system has no solution.
3
(a)( + ) =0
(c) The system has unique solution.
(b) I + A is invertible
(d) The system has infinite number of
solution (c) I + A is not invertible
(d) necessarily A = 0
[MS 2006]
[IISC 2007]
5