Page 16 - Digital Electronics by harish
P. 16
1.1.3 Binary codes
We use the decimal code to represent numbers. Digital electronic circuits in computers and
calculators use mostly the binary code to represent numbers. Many other special codes are
used in digital electronics to represent numbers, letters, and punctuation marks and control
characters. These special codes are generally called binary codes. Some of the special binary
codes are BCD code, Gray code, and Excess 3 code.
BCD Code (Natural BCD code)
BCD is an abbreviation for Binary-Coded Decimal. In this code, decimal digits 0 through 9
are represented by their binary equivalents using 4 bits (binary digits) individually. For
example, the decimal number 429 is expressed in BCD as follows:
Decimal number : 4 2 9
BCD number : 0100 0010 1001
The lowest BCD digit is 0000 and the highest BCD digit is 1001. In general, BCD codes are
also called 8421 code. The main advantage of 8421 code is that converting to and from
decimal numbers is very easy.
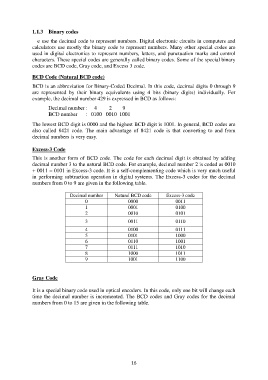
Excess-3 Code
This is another form of BCD code. The code for each decimal digit is obtained by adding
decimal number 3 to the natural BCD code. For example, decimal number 2 is coded as 0010
+ 0011 = 0101 in Excess-3 code. It is a self-complementing code which is very much useful
in performing subtraction operation in digital systems. The Excess-3 codes for the decimal
numbers from 0 to 9 are given in the following table.
Decimal number Natural BCD code Excess-3 code
0 0000 0011
1 0001 0100
2 0010 0101
3 0011 0110
4 0100 0111
5 0101 1000
6 0110 1001
7 0111 1010
8 1000 1011
9 1001 1100
Gray Code
It is a special binary code used in optical encoders. In this code, only one bit will change each
time the decimal number is incremented. The BCD codes and Gray codes for the decimal
numbers from 0 to 15 are given in the following table.
16