Page 43 - Digital Electronics by harish
P. 43
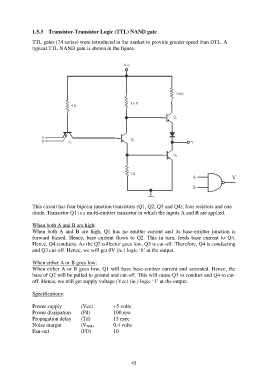
1.5.3 Transistor-Transistor Logic (TTL) NAND gate
TTL gates (74 series) were introduced in the market to provide greater speed than DTL. A
typical TTL NAND gate is shown in the figure.
This circuit has four bipolar junction transistors (Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4), four resistors and one
diode. Transistor Q1 is a multi-emitter transistor in which the inputs A and B are applied.
When both A and B are high:
When both A and B are high, Q1 has no emitter current and its base-emitter junction is
forward biased. Hence, base current flows to Q2. This in turn, feeds base current to Q4.
Hence, Q4 conducts. As the Q2 collector goes low, Q3 is cut-off. Therefore, Q4 is conducting
and Q3 cut-off. Hence, we will get 0V (ie.) logic „0‟ at the output.
When either A or B goes low:
When either A or B goes low, Q1 will have base-emitter current and saturated. Hence, the
base of Q2 will be pulled to ground and cut-off. This will cause Q3 to conduct and Q4 to cut-
off. Hence, we will get supply voltage (Vcc) (ie.) logic „1‟ at the output.
Specifications:
Power supply (Vcc) +5 volts
Power dissipation (Pd) 100 mw
Propagation delay (Td) 15 nsec
Noise margin (V NM) 0.4 volts
Fan-out (FO) 10
43