Page 39 - analysis-and-interpretation-of-astronomical-sp
P. 39
Analysis and Interpretation of Astronomical Spectra 39
9 Visible Effects of Quantum Mechanics
9.1 Textbook Example Hydrogen Atom and Balmer Series
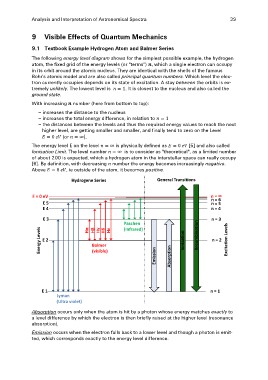
The following energy level diagram shows for the simplest possible example, the hydrogen
atom, the fixed grid of the energy levels (or "terms") , which a single electron can occupy
in its orbit around the atomic nucleus. They are identical with the shells of the famous
Bohr's atomic model and are also called principal quantum numbers. Which level the elec-
tron currently occupies depends on its state of excitation. A stay between the orbits is ex-
tremely unlikely. The lowest level is . It is closest to the nucleus and also called the
ground state.
With increasing number (here from bottom to top):
– increases the distance to the nucleus
– increases the total energy difference, in relation to
– the distances between the levels and thus the required energy values to reach the next
higher level, are getting smaller and smaller, and finally tend to zero on the Level
(or ).
The energy level E on the level is physically defined as [5] and also called
Ionisation Limit. The level number is to consider as "theoretical", as a limited number
of about 200 is expected, which a hydrogen atom in the interstellar space can really occupy
[6]. By definition, with decreasing number the energy becomes increasingly negative.
Above , ie outside of the atom, it becomes positive.
Hydrogene Series General Transitions
E = 0 eV nn == ∞
E5 6
E4 n=5
E3
n=4
E2
n=3
Energy Levels Paschen
Hα (Infrared)
Hβ
Hγ n=2
Hδ
HεBalmer
(visible)
Emission
Absorption
Ionization
Recombination
Excitation Levels
E1 n=1
Lyman
(Ultra violet)
Absorption occurs only when the atom is hit by a photon whose energy matches exactly to
a level difference by which the electron is then briefly raised at the higher level (resonance
absorption).
Emission occurs when the electron falls back to a lower level and though a photon is emit-
ted, which corresponds exactly to the energy level difference.