Page 250 - text book form physics kssm 2020
P. 250
Activity 6.4 Algorithms
Aim: To discuss the relationship between critical angle and refractive index
Instructions:
1. Work in pairs.
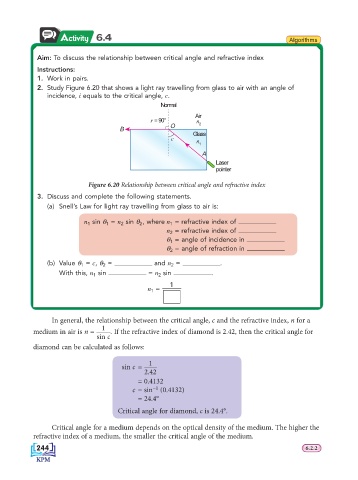
2. Study Figure 6.20 that shows a light ray travelling from glass to air with an angle of
incidence, i equals to the critical angle, c.
Normal
Air
r = 90° n 2
B O
Glass
c n
1
A
Laser
pointer
Figure 6.20 Relationship between critical angle and refractive index
3. Discuss and complete the following statements.
(a) Snell’s Law for light ray travelling from glass to air is:
n sin θ = n sin θ , where n = refractive index of
1
1
2
2
1
n = refractive index of
2
θ = angle of incidence in
1
θ = angle of refraction in
2
(b) Value θ = c, θ = and n = .
2
2
1
With this, n sin = n sin .
1
2
1
n =
1
In general, the relationship between the critical angle, c and the refractive index, n for a
1
medium in air is n = . If the refractive index of diamond is 2.42, then the critical angle for
sin c
diamond can be calculated as follows:
1
sin c =
2.42
= 0.4132
−1
c = sin (0.4132)
= 24.4°
Critical angle for diamond, c is 24.4°.
Critical angle for a medium depends on the optical density of the medium. The higher the
refractive index of a medium, the smaller the critical angle of the medium.
244
244 6.2.2
6.2.2