Page 255 - text book form physics kssm 2020
P. 255
Chapter 6
Light and Optics
Solving Problems Involving Total Internal Reflection
Example 1
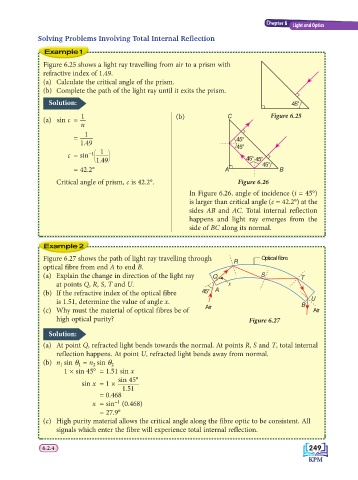
Figure 6.25 shows a light ray travelling from air to a prism with
refractive index of 1.49.
(a) Calculate the critical angle of the prism.
(b) Complete the path of the light ray until it exits the prism.
Solution: 45°
1 (b) C
(a) sin c = Figure 6.25
n
1
= 45°
1.49 45°
1
c = sin −1 1.49 45° 45°
= 42.2° A 45° B
Critical angle of prism, c is 42.2°. Figure 6.26
In Figure 6.26, angle of incidence (i = 45°)
is larger than critical angle (c = 42.2°) at the
sides AB and AC. Total internal reflection
happens and light ray emerges from the
side of BC along its normal.
Example 2
Figure 6.27 shows the path of light ray travelling through R Optical fibre
optical fibre from end A to end B.
(a) Explain the change in direction of the light ray Q S T
at points Q, R, S, T and U. x
(b) If the refractive index of the optical fibre 45° A
is 1.51, determine the value of angle x. B U
(c) Why must the material of optical fibres be of Air Air
high optical purity?
Figure 6.27
Solution:
(a) At point Q, refracted light bends towards the normal. At points R, S and T, total internal
reflection happens. At point U, refracted light bends away from normal.
(b) n sin θ = n sin θ 2
2
1
1
1 × sin 45° = 1.51 sin x
sin 45°
sin x = 1 ×
1.51
= 0.468
−1
x = sin (0.468)
= 27.9°
(c) High purity material allows the critical angle along the fibre optic to be consistent. All
signals which enter the fibre will experience total internal reflection.
249
6.2.4 249
6.2.4