Page 172 - Ultimate Visual Dictionary (DK)
P. 172
ANIMALS
Arachnids
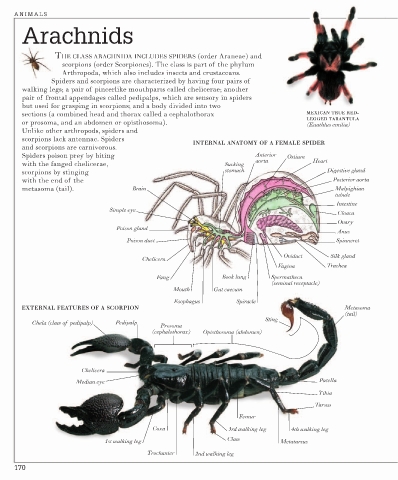
THE CLASS ARACHNIDA INCLUDES SPIDERS (order Araneae) and
scorpions (order Scorpiones). The class is part of the phylum
Arthropoda, which also includes insects and crustaceans.
Spiders and scorpions are characterized by having four pairs of
walking legs; a pair of pincerlike mouthparts called chelicerae; another
pair of frontal appendages called pedipalps, which are sensory in spiders
but used for grasping in scorpions; and a body divided into two
sections (a combined head and thorax called a cephalothorax MEXICAN TRUE RED-
LEGGED TARANTULA
or prosoma, and an abdomen or opisthosoma). (Euathlus emilia)
Unlike other arthropods, spiders and
scorpions lack antennae. Spiders
INTERNAL ANATOMY OF A FEMALE SPIDER
and scorpions are carnivorous.
Spiders poison prey by biting Anterior Ostium
aorta Heart
with the fanged chelicerae, Sucking
scorpions by stinging stomach Digestive gland
with the end of the Posterior aorta
metasoma (tail). Brain Malpighian
tubule
Intestine
Simple eye
Cloaca
Ovary
Poison gland
Anus
Poison duct Spinneret
Oviduct Silk gland
Chelicera
Vagina Trachea
Fang Book lung Spermatheca
(seminal receptacle)
Mouth Gut caecum
Esophagus Spiracle
EXTERNAL FEATURES OF A SCORPION Metasoma
(tail)
Sting
Chela (claw of pedipalp) Pedipalp
Prosoma
(cephalothorax) Opisthosoma (abdomen)
Chelicera
Median eye Patella
Tibia
Tarsus
Femur
Coxa 3rd walking leg 4th walking leg
1st walking leg Claw Metatarsus
Trochanter 2nd walking leg
170