Page 176 - Ultimate Visual Dictionary (DK)
P. 176
ANIMALS
Starfish and
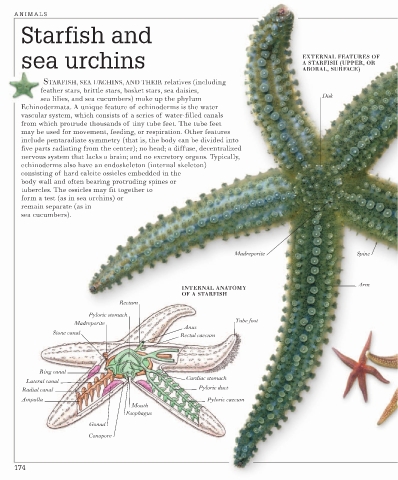
sea urchins EXTERNAL FEATURES OF
A STARFISH (UPPER, OR
ABORAL, SURFACE)
STARFISH, SEA URCHINS, AND THEIR relatives (including
feather stars, brittle stars, basket stars, sea daisies,
Disk
sea lilies, and sea cucumbers) make up the phylum
Echinodermata. A unique feature of echinoderms is the water
vascular system, which consists of a series of water-filled canals
from which protrude thousands of tiny tube feet. The tube feet
may be used for movement, feeding, or respiration. Other features
include pentaradiate symmetry (that is, the body can be divided into
five parts radiating from the center); no head; a diffuse, decentralized
nervous system that lacks a brain; and no excretory organs. Typically,
echinoderms also have an endoskeleton (internal skeleton)
consisting of hard calcite ossicles embedded in the
body wall and often bearing protruding spines or
tubercles. The ossicles may fit together to
form a test (as in sea urchins) or
remain separate (as in
sea cucumbers).
Madreporite Spine
Arm
INTERNAL ANATOMY
OF A STARFISH
Rectum
Pyloric stomach
Tube foot
Madreporite
Anus
Stone canal
Rectal caecum
Ring canal
Cardiac stomach
Lateral canal
Pyloric duct
Radial canal
Ampulla Pyloric caecum
Mouth
Esophagus
Gonad
Conopore
174