Page 178 - Ultimate Visual Dictionary (DK)
P. 178
ANIMALS
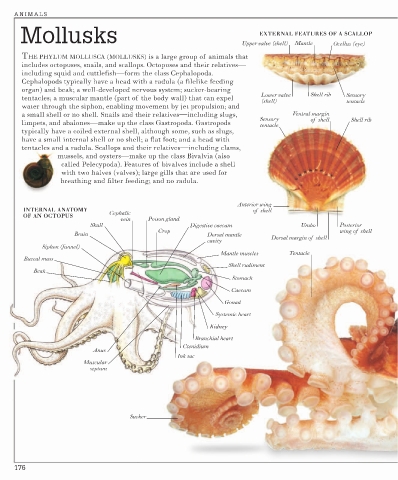
Mollusks Upper valve (shell) Mantle Ocellus (eye)
EXTERNAL FEATURES OF A SCALLOP
THE PHYLUM MOLLUSCA (MOLLUSKS) is a large group of animals that
includes octopuses, snails, and scallops. Octopuses and their relatives—
including squid and cuttlefish—form the class Cephalopoda.
Cephalopods typically have a head with a radula (a filelike feeding
organ) and beak; a well-developed nervous system; sucker-bearing
Lower valve Shell rib Sensory
tentacles; a muscular mantle (part of the body wall) that can expel
(shell) tentacle
water through the siphon, enabling movement by jet propulsion; and
a small shell or no shell. Snails and their relatives—including slugs, Ventral margin
Sensory of shell Shell rib
limpets, and abalones—make up the class Gastropoda. Gastropods
tentacle
typically have a coiled external shell, although some, such as slugs,
have a small internal shell or no shell; a flat foot; and a head with
tentacles and a radula. Scallops and their relatives—including clams,
mussels, and oysters—make up the class Bivalvia (also
called Pelecypoda). Features of bivalves include a shell
with two halves (valves); large gills that are used for
breathing and filter feeding; and no radula.
Anterior wing
INTERNAL ANATOMY of shell
Cephalic
OF AN OCTOPUS
vein Poison gland
Skull Digestive caecum Umbo Posterior
Crop wing of shell
Brain Dorsal mantle
cavity Dorsal margin of shell
Siphon (funnel)
Mantle muscles Tentacle
Buccal mass
Shell rudiment
Beak
Stomach
Caecum
Gonad
Systemic heart
Kidney
Branchial heart
Ctenidium
Anus
Ink sac
Muscular
septum
Sucker
176