Page 24 - Ultimate Visual Dictionary (DK)
P. 24
THE UNIVERSE
Stars
STARS ARE BODIES of hot,
glowing gas that are born in
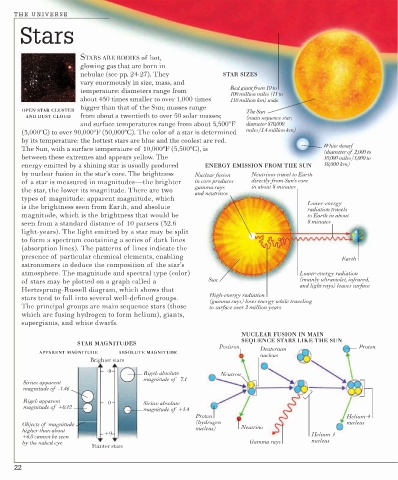
nebulae (see pp. 24-27). They STAR SIZES
vary enormously in size, mass, and
Red giant from 10 to
temperature: diameters range from
100 million miles (15 to
about 450 times smaller to over 1,000 times 150 million km) wide
bigger than that of the Sun; masses range
OPEN STAR CLUSTER The Sun
AND DUST CLOUD from about a twentieth to over 50 solar masses; (main sequence star;
and surface temperatures range from about 5,500ºF diameter 870,000
(3,000ºC) to over 90,000ºF (50,000ºC). The color of a star is determined miles/1.4 million km)
by its temperature: the hottest stars are blue and the coolest are red.
White dwarf
The Sun, with a surface temperature of 10,000ºF (5,500ºC), is
(diameter of 2,000 to
between these extremes and appears yellow. The 30,000 miles/3,000 to
energy emitted by a shining star is usually produced ENERGY EMISSION FROM THE SUN 50,000 km)
by nuclear fusion in the star’s core. The brightness Nuclear fusion Neutrinos travel to Earth
of a star is measured in magnitudes—the brighter in core produces directly from Sun’s core
gamma rays in about 8 minutes
the star, the lower its magnitude. There are two
and neutrinos
types of magnitude: apparent magnitude, which
Lower-energy
is the brightness seen from Earth, and absolute
radiation travels
magnitude, which is the brightness that would be to Earth in about
seen from a standard distance of 10 parsecs (32.6 8 minutes
light-years). The light emitted by a star may be split
to form a spectrum containing a series of dark lines
(absorption lines). The patterns of lines indicate the
presence of particular chemical elements, enabling Earth
astronomers to deduce the composition of the star’s
atmosphere. The magnitude and spectral type (color) Lower-energy radiation
of stars may be plotted on a graph called a Sun (mainly ultraviolet, infrared,
and light rays) leaves surface
Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, which shows that
High-energy radiation
stars tend to fall into several well-defined groups.
(gamma rays) loses energy while traveling
The principal groups are main sequence stars (those to surface over 2 million years
which are fusing hydrogen to form helium), giants,
supergiants, and white dwarfs.
NUCLEAR FUSION IN MAIN
SEQUENCE STARS LIKE THE SUN
STAR MAGNITUDES
Positron Deuterium Proton
APPARENT MAGNITUDE ABSOLUTE MAGNITUDE
nucleus
Brighter stars
-9 Rigel: absolute Neutron
magnitude of -7.1
Sirius: apparent
magnitude of -1.46
Rigel: apparent 0 Sirius: absolute
magnitude of +0.12
magnitude of +1.4
Proton Helium-4
(hydrogen nucleus
Objects of magnitude Neutrino
higher than about +9 nucleus)
+6.0 cannot be seen Helium-3
by the naked eye Gamma rays nucleus
Fainter stars
22