Page 299 - (DK) The Ultimate Visual Dictionary 2nd Ed.
P. 299
OCEANS AND SEAS
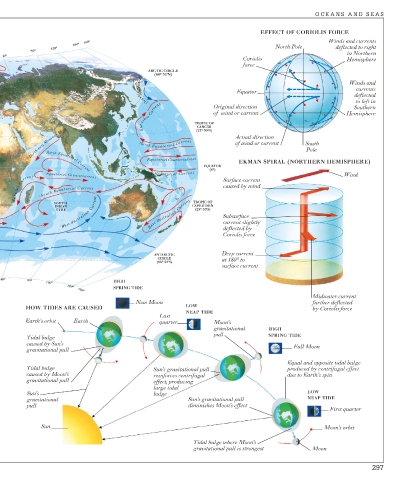
EFFECT OF CORIOLIS FORCE
180° Winds and currents
160°
120° North Pole deflected to right
80°
in Northern
40°
Coriolis Hemisphere
force
ARCTIC CIRCLE
(66° 32'N)
Oyashio Curren t Equator Winds and
currents
deflected
to left in
Current Original direction Hemisphere
Southern
of wind or current
Kuroshio TROPIC OF
CANCER
North-east Monsoon Drift North Equat orial Current Actual direction South
(23° 30'N)
of wind or current
Pole
Equatorial Countercurrent
EKMAN SPIRAL (NORTHERN HEMISPHERE)
EQUATOR
(0°)
North Equatorial Cu rrent
South Equat oria l Current
Wind
A gh u la s C u rr en t S outh Equa toria l Current caused by wind
Equatorial Countercurrent
Surface current
West Aus tr alian Current East Australia n Current Subsurface
SOUTH TROPIC OF
INDIAN CAPRICORN
GYRE (23° 30'S)
current slightly
deflected by
Coriolis force
Deep current
ANTARCTIC
CIRCLE at 180° to
(66° 32'S)
surface current
40° 80° HIGH
120°
160°
SPRING TIDE
180°
Midwater current
New Moon further deflected
HOW TIDES ARE CAUSED LOW by Coriolis force
NEAP TIDE
Last
Earth’s orbit Earth quarter Moon’s
gravitational HIGH
pull SPRING TIDE
Tidal bulge
caused by Sun’s Full Moon
gravitational pull
Equal and opposite tidal bulge
Tidal bulge Sun’s gravitational pull produced by centrifugal effect
caused by Moon’s reinforces centrifugal due to Earth’s spin
gravitational pull effect, producing
large tidal
Sun’s bulge LOW
gravitational Sun’s gravitational pull NEAP TIDE
pull diminishes Moon’s effect
First quarter
Sun Moon’s orbit
Tidal bulge where Moon’s
gravitational pull is strongest Moon
297