Page 296 - (DK) The Ultimate Visual Dictionary 2nd Ed.
P. 296
GEOLOGY, GEOGRAPHY, AND METEOROLOGY
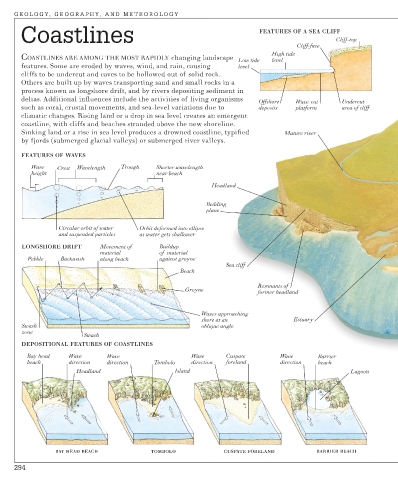
Coastlines FEATURES OF A SEA CLIFF
Cliff-top
Cliff-face
High tide
COASTLINES ARE AMONG THE MOST RAPIDLY changing landscape
Low tide level
features. Some are eroded by waves, wind, and rain, causing level
cliffs to be undercut and caves to be hollowed out of solid rock.
Others are built up by waves transporting sand and small rocks in a
process known as longshore drift, and by rivers depositing sediment in
deltas. Additional influences include the activities of living organisms
Offshore Wave-cut Undercut
such as coral, crustal movements, and sea-level variations due to deposits platform area of cliff
climatic changes. Rising land or a drop in sea level creates an emergent
coastline, with cliffs and beaches stranded above the new shoreline.
Sinking land or a rise in sea level produces a drowned coastline, typified Mature river
by fjords (submerged glacial valleys) or submerged river valleys.
FEATURES OF WAVES
Wave Crest Wavelength Trough Shorter wavelength
height near beach
Headland
Bedding
plane
Circular orbit of water Orbit deformed into ellipse
and suspended particles as water gets shallower
LONGSHORE DRIFT Movement of Buildup
material of material
Pebble Backwash along beach against groyne
Sea cliff
Beach
Remnants of
Groyne
former headland
Waves approaching
shore at an Estuary
Swash oblique angle
zone
Swash
DEPOSITIONAL FEATURES OF COASTLINES
Bay head Wave Wave Wave Cuspate Wave Barrier
beach direction direction Tombolo direction foreland direction beach
Headland Island Lagoon
BAY HEAD BEACH TOMBOLO CUSPATE FORELAND BARRIER BEACH
294