Page 76 - How It Works - Book Of Amazing Answers To Curious Questions, Volume 05-15
P. 76
What is saliva?
Find out this frothy liquid’s
vital role in maintaining
human health
umans can produce an incredible two
litres (half a gallon) of saliva each day. It
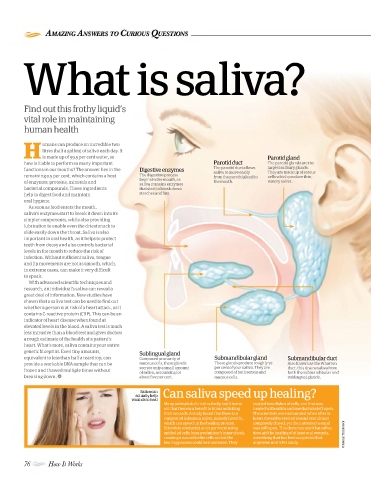
His made up of 99.5 per cent water, so Parotid gland
how is it able to perform so many important Parotid duct The parotid glands are the
functions in our mouths? The answer lies in the Digestive enzymes The parotid duct allows largest salivary glands.
saliva to move easily
They are made up of serous
remaining 0.5 per cent, which contains a host The digestion process from the parotid gland to cells which produce thin,
begins in the mouth, as
of enzymes, proteins, minerals and the mouth. watery saliva.
saliva contains enzymes
bacterial compounds. These ingredients that start to break down
help to digest food and maintain starches and fats.
oral hygiene.
As soon as food enters the mouth,
saliva’s enzymes start to break it down into its
simpler components, while also providing
lubrication to enable even the driest snack to
slide easily down the throat. Saliva is also
important in oral health, as it helps to protect
teeth from decay and also controls bacterial
levels in the mouth to reduce the risk of
infection. Without sufficient saliva, tongue
and lip movements are not as smooth, which,
in extreme cases, can make it very diffi cult
to speak.
With advanced scientific techniques and
research, an individual’s saliva can reveal a
great deal of information. New studies have
shown that a saliva test can be used to fi nd out
whether a person is at risk of a heart attack, as it
contains C-reactive protein (CRP). This can be an
indicator of heart disease when found at
elevated levels in the blood. A saliva test is much
less intrusive than a blood test and gives doctors
a rough estimate of the health of a patient’s
heart. What’s more, saliva contains your entire
genetic blueprint. Even tiny amounts, Sublingual gland
equivalent to less than half a teardrop, can Composed primarily of Submandibular gland Submandibular duct
provide a workable DNA sample that can be mucous cells, these glands These glands produce roughly 70 Also known as the Wharton
secrete only a small amount per cent of your saliva. They are duct, this drains saliva from
frozen and thawed multiple times without
of saliva, accounting for composed of both serous and both the submandibular and
breaking down. about five per cent. mucous cells. sublingual glands.
Saliva can Can saliva speed up healing?
actually help
wounds to heal
Many animals do it instinctively, but it turns created two dishes of cells, one that was
out that there is a benefit to humans licking treated with saliva and one that was left open.
their wounds. A study found that there is a The scientists were astounded when after 16
compound in human saliva, namely histatin, hours the saliva-treated wound was almost
which can speed up the healing process. completely closed, yet the untreated wound
Scientists conducted an experiment using was still open. This demonstrated that saliva
epithelial cells from a volunteer’s inner cheek, does aid the healing of at least oral wounds, © Alamy; Thinkstock
creating a wound in the cells so that the something that has been suspected but
healing process could be monitored. They unproven until this study.
76 How It Works