Page 44 - (DK Eyewitness) Travel Guide - India
P. 44
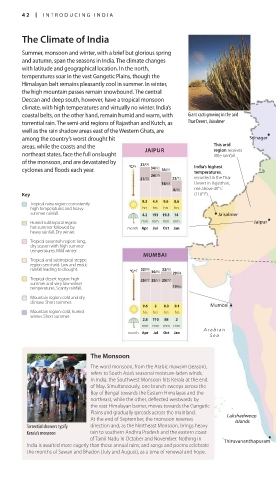
42 INTRODUCING INDIA
The Climate of India
Summer, monsoon and winter, with a brief but glorious spring
and autumn, span the seasons in India. The climate changes
with latitude and geographical location. In the north,
temperatures soar in the vast Gangetic Plains, though the
Himalayan belt remains pleasantly cool in summer. In winter,
the high mountain passes remain snowbound. The central
Deccan and deep south, however, have a tropical monsoon
climate, with high temperatures and virtually no winter. India’s
coastal belts, on the other hand, remain humid and warm, with Giant cacti growing in the arid
torrential rain. The semi-arid regions of Rajasthan and Kutch, as Thar Desert, Jaisalmer
well as the rain shadow areas east of the Western Ghats, are
•
among the country’s worst drought hit Srinagar
areas, while the coasts and the JAIPUR This arid
region receives
northeast states, face the full onslaught little rainfall.
of the monsoon, and are devastated by 37/99
cyclones and floods each year. °C/ºF 34/93 33/91 India’s highest
temperatures,
26/79
21/70 22/72 recorded in the Thar
18/64 Desert in Rajasthan,
8/46 rise above 48° C
Key (118° F).
9.3 4.4 9.6 8.6 • Delhi
Tropical rainy region: consistently
high temperatures and heavy hrs hrs hrs hrs
summer rainfall. 4.2 193 19.3 14 • Jaisalmer
Humid subtropical region: mm mm mm mm Jaipur •
hot summer followed by month Apr Jul Oct Jan
heavy rainfall. Dry winter.
Cherrapunji
Tropical savannah region: long, •
dry season with high summer
temperatures. Mild winter.
MUMBAI
Tropical and subtropical steppe
region: semi-arid. Low and erratic • Bhopal Tropic of Cancer
rainfall leading to drought. °C/ºF 32/90 30/86 32/90 29/84 Kolkata •
Tropical desert region: high 25/77 25/77 25/77
summer and very low winter
temperatures. Scanty rainfall. 19/66
INDIA
Mountain region: cold and dry
climate. Short summer.
9.6 2 8.3 9.1 Mumbai •
Mountain region: cold, humid hrs hrs hrs hrs Bay of
winter. Short summer. Bengal
2.8 710 88 2
mm mm mm mm Hyderabad
Arabian •
month Apr Jul Oct Jan
Sea
The Monsoon
The word monsoon, from the Arabic mawsim (season),
refers to South Asia’s seasonal moisture-laden winds.
In India, the Southwest Monsoon hits Kerala at the end • Chennai
of May. Simultaneously, one branch sweeps across the
Bay of Bengal towards the Eastern Himalayas and the
northeast, while the other, deflected westwards by
the vast Himalayan barrier, moves towards the Gangetic
Plains and gradually spreads across the mainland. Lakshadweep
At the end of September, the monsoon reverses Islands Andaman &
Torrential showers typify direction and, as the Northeast Monsoon, brings heavy Nicobar Islands
Kerala’s monsoon rain to southern Andhra Pradesh and the eastern coast
of Tamil Nadu in October and November. Nothing in Thiruvananthapuram •
India is awaited more eagerly than these annual rains; and songs and poems celebrate
the months of Sawan and Bhadon (July and August), as a time of renewal and hope.
042-043_EW_India.indd 42 26/04/17 11:52 am