Page 178 - Nilam_Publication_module_Chemistry_Form.pdf
P. 178
MODULE • Chemistry Form 4
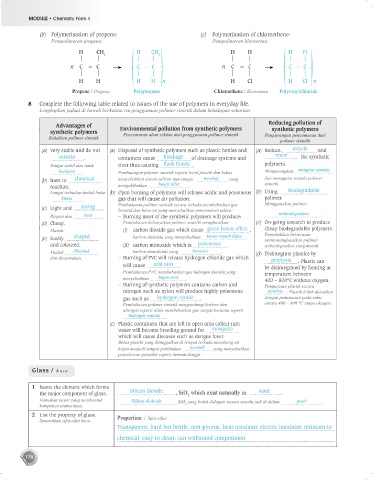
(b) Polymerisation of propene: (c) Polymerisation of chloroethene:
Pempolimeran propena: Pempolimeran kloroetena:
H CH 3 H CH 3 H H H H
n C = C – C – C – n C = C – C – C –
H H H H n H Cl H Cl n
Propene / Propena Polypropene Chloroethene / Kloroetena Polyvinylchloride
8 Complete the following table related to issues of the use of polymers in everyday life.
Lengkapkan jadual di bawah berkaitan isu penggunaan polimer sintetik dalam kehidupan seharian.
Reducing pollution of
Advantages of
synthetic polymers Environmental pollution from synthetic polymers synthetic polymers
Kebaikan polimer sintetik Pencemaran alam sekitar dari penggunaan polimer sintetik Pengurangan pencemaran dari
polimer sintetik
(a) Very stable and do not (a) Disposal of synthetic polymers such as plastic bottles and (a) Reduce, recycle and
corrode . containers cause blockage of drainage systems and reuse the synthetic
Sangat stabil dan tidak river thus causing flash floods . polymers.
berkarat . Pembuangan polimer sintetik seperti botol plastik dan bekas Mengurangkan, mengitar semula
(b) Inert to chemical menyebabkan sistem saliran dan sungai tersekat yang dan mengguna semula polimer
reaction. mengakibatkan banjir kilat . sintetik.
Lengai terhadap tindak balas (b) Open burning of polymers will release acidic and poisonous (b) Using biodegradable
kimia . gas that will cause air pollution: polimer.
(c) Light and strong . Pembakaran polimer sintetik secara terbuka membebaskan gas Menggunakan polimer
berasid dan beracun yang menyebabkan pencemaran udara:
Ringan dan kuat . – Burning most of the synthetic polymers will produce: terbiodegradasi .
(d) Cheap. Pembakaran kebanyakan polimer sintetik menghasilkan: (c) On-going research to produce
Murah. (i) carbon dioxide gas which cause green house effect . cheap biodegradable polymers.
(e) Easily shaped karbon dioksida yang menyebabkan kesan rumah hijau . Penyelidikan berterusan
untuk menghasilkan polimer
and coloured. (ii) carbon monoxide which is poisonous . terbiodegradasi yang murah.
Mudah dibentuk karbon monoksida yang beracun . (d) Disintegrate plastics by
dan diwarnakan. – Burning of PVC will release hydrogen chloride gas which pyrolysis : Plastic can
will cause acid rain . be disintegrated by heating at
Pembakaran PVC membebaskan gas hidrogen klorida yang temperature between
menyebabkan hujan asid . 400 – 800°C without oxygen.
– Burning of synthetic polymers contains carbon and Penguraian plastik secara
nitrogen such as nylon will produce highly poisonous pirolisis : Plastik boleh diuraikan
gas such as hydrogen cynide . dengan pemanasan pada suhu
Pembakaran polimer sintetik mengandungi karbon dan antara 400 – 800 °C tanpa oksigen.
nitrogen seperti nilon membebaskan gas sangat beracun seperti
hidrogen sianida .
(c) Plastic containers that are left in open area collect rain
water will become breeding ground for mosquito
which will cause diseases such as dengue fever.
Bekas plastik yang ditinggalkan di tempat terbuka menakung air
hujan menjadi tempat pembiakan nyamuk yang menyebabkan
penyebaran penyakit seperti demam denggi.
Glass / Kaca
1 Name the element which forms
the major component of glass. Silicon dioxide , SiO which exist naturally in sand .
2
Namakan unsur yang membentuk Silikon dioksida , SiO yang boleh didapati secara semula jadi di dalam pasir .
komponen utama kaca. 2
2 List the property of glass.
Senaraikan sifat-sifat kaca. Properties: / Sifat-sifat:
Transparent, hard but brittle, non-porous, heat insulator, electric insulator, resistant to
chemical, easy to clean, can withstand compression
176
Nilam Publication Sdn. Bhd.
08-Chem F4 (3p).indd 176 12/9/2011 5:54:31 PM