Page 240 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 240
196 SEcTioN ii Microbiology ` microbiology—aNtimicrobials Microbiology ` microbiology—aNtimicrobials
Antimycobacterial therapy
bacteriUm ProPHylaXis treatmeNt
M tuberculosis Isoniazid Rifampin, Isoniazid, Pyrazinamide,
Ethambutol (RIPE for treatment)
M avium–intracellulare Azithromycin, rifabutin Azithromycin or clarithromycin + ethambutol
Can add rifabutin or ciprofloxacin
M leprae N/A Long-term treatment with dapsone and rifampin
for tuberculoid form
Add clofazimine for lepromatous form
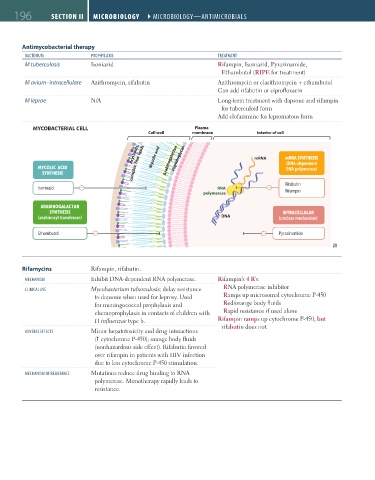
MYCOBACTERIAL CELL Plasma
Cell wall membrane Interior of cell
Acyl lipids,
Acyl lipids, Mycolic acid Arabinogalactan Peptidoglycan mRNA mRNA SYNTHESIS
Acyl lipids,
Acyl lipids,
complex free lipids
Arabinogalactan
Peptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan
complex free lipids
Peptidoglycan
complex free lipids
Peptidoglycan
Arabinogalactan
Arabinogalactan
Mycolic acid
Mycolic acid
Mycolic acid
Mycolic acid
MYCOLIC ACID complex free lipids Arabinogalactan (DNA-dependent
RNA polymerase)
SYNTHESIS
Isoniazid – RNA – Rifabutin
polymerase Rifampin
ARABINOGALACTAN
SYNTHESIS INTRACELLULAR
(arabinosyl transferase) DNA (unclear mechanism)
Ethambutol – – Pyrazinamide
Rifamycins Rifampin, rifabutin.
mecHaNism Inhibit DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Rifampin’s 4 R’s:
cliNical Use Mycobacterium tuberculosis; delay resistance RNA polymerase inhibitor
to dapsone when used for leprosy. Used Ramps up microsomal cytochrome P-450
for meningococcal prophylaxis and Red/orange body fluids
chemoprophylaxis in contacts of children with Rapid resistance if used alone
H influenzae type b. Rifampin ramps up cytochrome P-450, but
rifabutin does not.
aDVerse eFFects Minor hepatotoxicity and drug interactions
( cytochrome P-450); orange body fluids
(nonhazardous side effect). Rifabutin favored
over rifampin in patients with HIV infection
due to less cytochrome P-450 stimulation.
mecHaNism oF resistaNce Mutations reduce drug binding to RNA
polymerase. Monotherapy rapidly leads to
resistance.
FAS1_2019_03-Microbiology.indd 196 11/14/19 12:22 PM