Page 241 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 241
Microbiology ` microbiology—aNtimicrobials Microbiology ` microbiology—aNtimicrobials SEcTioN ii 197
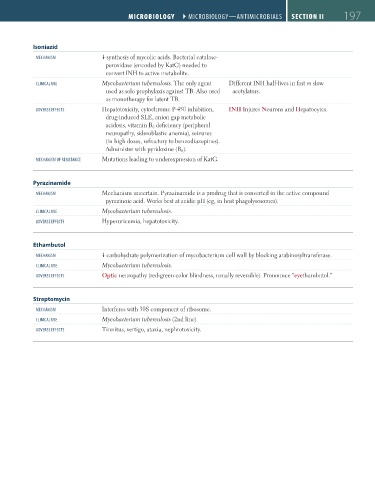
Isoniazid
mecHaNism synthesis of mycolic acids. Bacterial catalase-
peroxidase (encoded by KatG) needed to
convert INH to active metabolite.
cliNical Use Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The only agent Different INH half-lives in fast vs slow
used as solo prophylaxis against TB. Also used acetylators.
as monotherapy for latent TB.
aDVerse eFFects Hepatotoxicity, cytochrome P-450 inhibition, INH Injures Neurons and Hepatocytes.
drug-induced SLE, anion gap metabolic
acidosis, vitamin B 6 deficiency (peripheral
neuropathy, sideroblastic anemia), seizures
(in high doses, refractory to benzodiazepines).
Administer with pyridoxine (B 6 ).
mecHaNism oF resistaNce Mutations leading to underexpression of KatG.
Pyrazinamide
mecHaNism Mechanism uncertain. Pyrazinamide is a prodrug that is converted to the active compound
pyrazinoic acid. Works best at acidic pH (eg, in host phagolysosomes).
cliNical Use Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
aDVerse eFFects Hyperuricemia, hepatotoxicity.
Ethambutol
mecHaNism carbohydrate polymerization of mycobacterium cell wall by blocking arabinosyltransferase.
cliNical Use Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
aDVerse eFFects Optic neuropathy (red-green color blindness, usually reversible). Pronounce “eyethambutol.”
Streptomycin
mecHaNism Interferes with 30S component of ribosome.
cliNical Use Mycobacterium tuberculosis (2nd line).
aDVerse eFFects Tinnitus, vertigo, ataxia, nephrotoxicity.
FAS1_2019_03-Microbiology.indd 197 11/14/19 12:22 PM