Page 238 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 238
194 SEcTioN ii Microbiology ` microbiology—aNtimicrobials Microbiology ` microbiology—aNtimicrobials
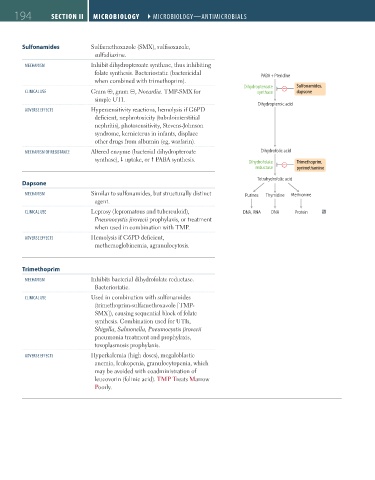
Sulfonamides Sulfamethoxazole (SMX), sulfisoxazole,
sulfadiazine.
mecHaNism Inhibit dihydropteroate synthase, thus inhibiting
folate synthesis. Bacteriostatic (bactericidal PABA + Pteridine
when combined with trimethoprim).
Dihydropteroate Sulfonamides,
cliNical Use Gram ⊕, gram ⊝, Nocardia. TMP-SMX for synthase dapsone
simple UTI.
Dihydropteroic acid
aDVerse eFFects Hypersensitivity reactions, hemolysis if G6PD
deficient, nephrotoxicity (tubulointerstitial
nephritis), photosensitivity, Stevens-Johnson
syndrome, kernicterus in infants, displace
other drugs from albumin (eg, warfarin).
mecHaNism oF resistaNce Altered enzyme (bacterial dihydropteroate Dihydrofolic acid
synthase), uptake, or PABA synthesis. Dihydrofolate Trimethoprim,
reductase pyrimethamine
Tetrahydrofolic acid
Dapsone
mecHaNism Similar to sulfonamides, but structurally distinct Purines Thymidine Methionine
agent.
cliNical Use Leprosy (lepromatous and tuberculoid), DNA, RNA DNA Protein
Pneumocystis jirovecii prophylaxis, or treatment
when used in combination with TMP.
aDVerse eFFects Hemolysis if G6PD deficient,
methemoglobinemia, agranulocytosis.
Trimethoprim
mecHaNism Inhibits bacterial dihydrofolate reductase.
Bacteriostatic.
cliNical Use Used in combination with sulfonamides
(trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole [TMP-
SMX]), causing sequential block of folate
synthesis. Combination used for UTIs,
Shigella, Salmonella, Pneumocystis jirovecii
pneumonia treatment and prophylaxis,
toxoplasmosis prophylaxis.
aDVerse eFFects Hyperkalemia (high doses), megaloblastic
anemia, leukopenia, granulocytopenia, which
may be avoided with coadministration of
leucovorin (folinic acid). TMP Treats Marrow
Poorly.
FAS1_2019_03-Microbiology.indd 194 11/14/19 12:22 PM