Page 276 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 276
232 SEcTIoN II Pharmacology ` PHARMACOLOGY—PHARMACOKINETICS ANd PHARMACOdYNAMICS Pharmacology ` PHARMACOLOGY—PHARMACOKINETICS ANd PHARMACOdYNAMICS
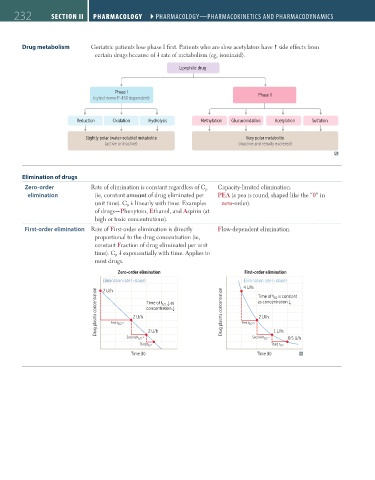
Drug metabolism Geriatric patients lose phase I first. Patients who are slow acetylators have side effects from
certain drugs because of rate of metabolism (eg, isoniazid).
Lipophilic drug
Phase I
(cytochrome P-450 dependent) Phase II
Reduction Oxidation Hydrolysis Methylation Glucuronidation Acetylation Sulfation
Slightly polar (water-soluble) metabolite Very polar metabolite
(active or inactive) (inactive and renally excreted)
Elimination of drugs
Zero-order Rate of elimination is constant regardless of C p Capacity-limited elimination.
elimination (ie, constant amount of drug eliminated per PEA (a pea is round, shaped like the “0” in
unit time). C p linearly with time. Examples zero-order).
of drugs—Phenytoin, Ethanol, and Aspirin (at
high or toxic concentrations).
First-order elimination Rate of First-order elimination is directly Flow-dependent elimination.
proportional to the drug concentration (ie,
constant Fraction of drug eliminated per unit
time). C p exponentially with time. Applies to
most drugs.
Zero-order elimination First-order elimination
Elimination rate (=slope) Elimination rate (=slope)
4 U/h Time of t 1/2 is constant
Drug plasma concentration First t 1/2 > 2 U/h Time of t 1/2 as ↑ Drug plasma concentration First t 1/2 == as concentration ↑
2 U/h
concentration
↑
2 U/h
Second t 1/2 > 2 U/h Second t 1/2 = 1 U/h 0.5 U/h
Third t 1/2 Third t 1/2
Time (h) Time (h)
FAS1_2019_05-Pharmacology.indd 232 11/7/19 4:08 PM