Page 278 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 278
234 SEcTIoN II Pharmacology ` PHARMACOLOGY—PHARMACOKINETICS ANd PHARMACOdYNAMICS Pharmacology ` PHARMACOLOGY—PHARMACOKINETICS ANd PHARMACOdYNAMICS
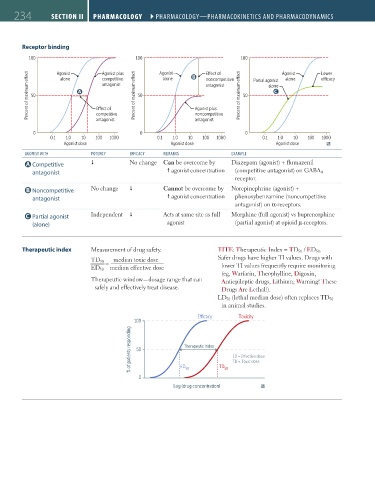
Receptor binding
100 100 100
Agonist Agonist plus Agonist E ect of Agonist Lower
alone competitive alone B noncompetitive Partial agonist alone
antagonist antagonist alone
A C
50 50 50
Agonist plus
competitive noncompetitive
antagonist antagonist
0 0 0
0.1 1.0 10 100 1000 0.1 1.0 10 100 1000 0.1 1.0 10 100 1000
Agonist dose Agonist dose Agonist dose
AGONIST WITH POTENCY EFFICACY REMARKS EXAMPLE
A Competitive No change Can be overcome by Diazepam (agonist) + flumazenil
antagonist agonist concentration (competitive antagonist) on GABA A
receptor.
B Noncompetitive No change Cannot be overcome by Norepinephrine (agonist) +
antagonist agonist concentration phenoxybenzamine (noncompetitive
antagonist) on α-receptors.
C Partial agonist Independent Acts at same site as full Morphine (full agonist) vs buprenorphine
(alone) agonist (partial agonist) at opioid μ-receptors.
Therapeutic index Measurement of drug safety. TITE: Therapeutic Index = TD 50 / ED 50 .
TD 50 median toxic dose Safer drugs have higher TI values. Drugs with
=
ED 50 median effective dose lower TI values frequently require monitoring
(eg, Warfarin, Theophylline, Digoxin,
Therapeutic window—dosage range that can Antiepileptic drugs, Lithium; Warning! These
safely and effectively treat disease. Drugs Are Lethal!).
LD 50 (lethal median dose) often replaces TD 50
in animal studies.
E cacy Toxicity
100
% of patients responding 50 Therapeutic index ED = E ective dose
TD = Toxic dose
0 ED 50 TD 50
Log (drug concentration)
FAS1_2019_05-Pharmacology.indd 234 11/7/19 4:08 PM