Page 277 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 277
Pharmacology ` PHARMACOLOGY—PHARMACOKINETICS ANd PHARMACOdYNAMICS Pharmacology ` PHARMACOLOGY—PHARMACOKINETICS ANd PHARMACOdYNAMICS SEcTIoN II 233
Urine pH and drug Ionized species are trapped in urine and cleared quickly. Neutral forms can be reabsorbed.
elimination
Weak acids Examples: phenobarbital, methotrexate, aspirin (salicylates). Trapped in basic environments. Treat
overdose with sodium bicarbonate to alkalinize urine.
–
RCOOH RCOO + H +
(lipid soluble) (trapped)
Weak bases Examples: TCAs, amphetamines. Trapped in acidic environments. Treat overdose with ammonium
chloride to acidify urine.
RNH 3 RNH 2 + H +
+
(trapped) (lipid soluble)
TCA toxicity is generally treated with sodium bicarbonate to overcome the sodium channel-
blocking activity of TCAs, but not for accelerating drug elimination.
pKa pH at which drugs (weak acid or base) are 50% ionized and 50% nonionized. The pKa represents
the strength of the weak acid or base.
Efficacy vs potency
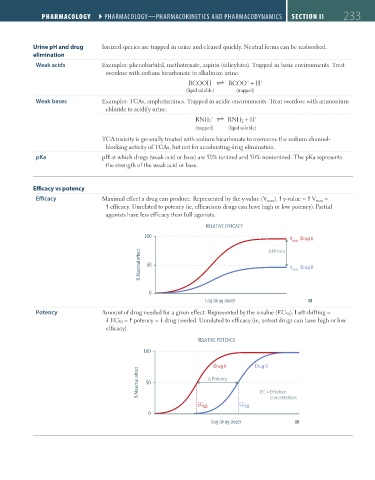
Efficacy Maximal effect a drug can produce. Represented by the y-value (V max ). y-value = V max =
efficacy. Unrelated to potency (ie, efficacious drugs can have high or low potency). Partial
agonists have less efficacy than full agonists.
RELATIVE EFFICACY
100
V
max Drug A
E cacy
% Maximal e ect 50 V max Drug B
0
Log (drug dose)
Potency Amount of drug needed for a given effect. Represented by the x-value (EC 50 ). Left shifting =
EC 50 = potency = drug needed. Unrelated to efficacy (ie, potent drugs can have high or low
efficacy).
RELATIVE POTENCY
100
Drug A Drug B
% Maximal e
ect 50 Potency EC = E
ective
EC 50 EC 50 concentration
0
Log (drug dose)
FAS1_2019_05-Pharmacology.indd 233 11/7/19 4:08 PM