Page 526 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 526
482 section iii Musculoskeletal, skin, and connective tissue ` dERmatology Musculoskeletal, skin, and connective tissue ` dERmatology
Miscellaneous skin disorders
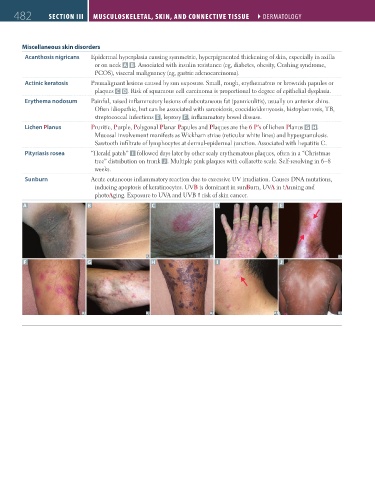
Acanthosis nigricans Epidermal hyperplasia causing symmetric, hyperpigmented thickening of skin, especially in axilla
or on neck A B . Associated with insulin resistance (eg, diabetes, obesity, Cushing syndrome,
PCOS), visceral malignancy (eg, gastric adenocarcinoma).
Actinic keratosis Premalignant lesions caused by sun exposure. Small, rough, erythematous or brownish papules or
plaques C D. Risk of squamous cell carcinoma is proportional to degree of epithelial dysplasia.
Erythema nodosum Painful, raised inflammatory lesions of subcutaneous fat (panniculitis), usually on anterior shins.
Often idiopathic, but can be associated with sarcoidosis, coccidioidomycosis, histoplasmosis, TB,
streptococcal infections E , leprosy F , inflammatory bowel disease.
Lichen Planus Pruritic, Purple, Polygonal Planar Papules and Plaques are the 6 P’s of lichen Planus G H.
Mucosal involvement manifests as Wickham striae (reticular white lines) and hypergranulosis.
Sawtooth infiltrate of lymphocytes at dermal-epidermal junction. Associated with hepatitis C.
Pityriasis rosea “Herald patch” I followed days later by other scaly erythematous plaques, often in a “Christmas
tree” distribution on trunk J . Multiple pink plaques with collarette scale. Self-resolving in 6–8
weeks.
Sunburn Acute cutaneous inflammatory reaction due to excessive UV irradiation. Causes DNA mutations,
inducing apoptosis of keratinocytes. UVB is dominant in sunBurn, UVA in tAnning and
photoAging. Exposure to UVA and UVB risk of skin cancer.
A B C D E
F G H I J
FAS1_2019_11-Musculo.indd 482 11/7/19 5:24 PM