Page 593 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 593
Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—PhArmACology Neurology aNd Special SeNSeS ` neurology—PhArmACology SecTioN iii 549
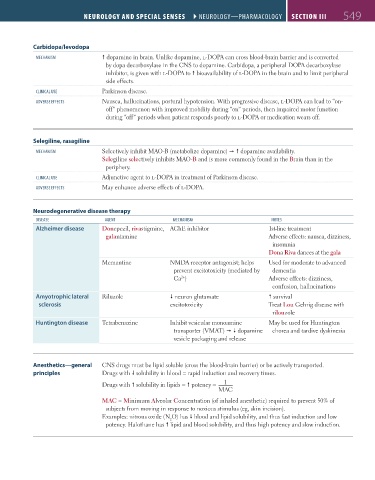
Carbidopa/levodopa
meChAnism dopamine in brain. Unlike dopamine, l-DOPA can cross blood-brain barrier and is converted
by dopa decarboxylase in the CNS to dopamine. Carbidopa, a peripheral DOPA decarboxylase
inhibitor, is given with l-DOPA to bioavailability of l-DOPA in the brain and to limit peripheral
side effects.
CliniCAl use Parkinson disease.
AdVerse eFFeCts Nausea, hallucinations, postural hypotension. With progressive disease, l-DOPA can lead to “on-
off” phenomenon with improved mobility during “on” periods, then impaired motor function
during “off” periods when patient responds poorly to l-DOPA or medication wears off.
Selegiline, rasagiline
meChAnism Selectively inhibit MAO-B (metabolize dopamine) dopamine availability.
Selegiline selectively inhibits MAO-B and is more commonly found in the Brain than in the
periphery.
CliniCAl use Adjunctive agent to l-DOPA in treatment of Parkinson disease.
AdVerse eFFeCts May enhance adverse effects of l-DOPA.
Neurodegenerative disease therapy
diseAse Agent meChAnism notes
Alzheimer disease Donepezil, rivastigmine, AChE inhibitor 1st-line treatment
galantamine Adverse effects: nausea, dizziness,
insomnia
Dona Riva dances at the gala
Memantine NMDA receptor antagonist; helps Used for moderate to advanced
prevent excitotoxicity (mediated by dementia
2+
Ca ) Adverse effects: dizziness,
confusion, hallucinations
Amyotrophic lateral Riluzole neuron glutamate survival
sclerosis excitotoxicity Treat Lou Gehrig disease with
rilouzole
Huntington disease Tetrabenazine Inhibit vesicular monoamine May be used for Huntington
transporter (VMAT) dopamine chorea and tardive dyskinesia
vesicle packaging and release
Anesthetics—general CNS drugs must be lipid soluble (cross the blood-brain barrier) or be actively transported.
principles Drugs with solubility in blood = rapid induction and recovery times.
1
Drugs with solubility in lipids = potency =
MAC
MAC = Minimum Alveolar Concentration (of inhaled anesthetic) required to prevent 50% of
subjects from moving in response to noxious stimulus (eg, skin incision).
Examples: nitrous oxide (N O) has blood and lipid solubility, and thus fast induction and low
2
potency. Halothane has lipid and blood solubility, and thus high potency and slow induction.
FAS1_2019_12-Neurol.indd 549 11/8/19 7:40 AM