Page 615 - First Aid for the USMLE Step 1 2020, Thirtieth edition [MedicalBooksVN.com]_Neat
P. 615
Psychiatry ` Psychiatry—Pathology Psychiatry ` Psychiatry—Pathology sEctiON iii 571
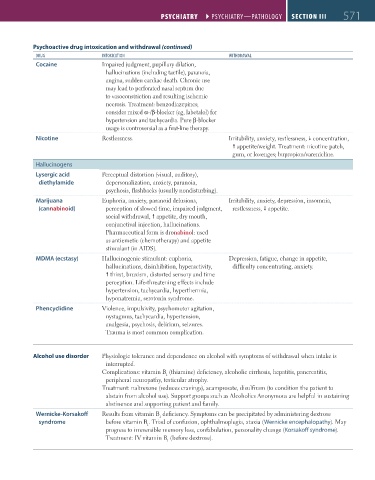
Psychoactive drug intoxication and withdrawal (continued)
DrUg iNtoXicatioN WithDraWal
Cocaine Impaired judgment, pupillary dilation,
hallucinations (including tactile), paranoia,
angina, sudden cardiac death. Chronic use
may lead to perforated nasal septum due
to vasoconstriction and resulting ischemic
necrosis. Treatment: benzodiazepines;
consider mixed α-/β-blocker (eg, labetalol) for
hypertension and tachycardia. Pure β-blocker
usage is controversial as a first-line therapy.
Nicotine Restlessness. Irritability, anxiety, restlessness, concentration,
appetite/weight. Treatment: nicotine patch,
gum, or lozenges; bupropion/varenicline.
Hallucinogens
Lysergic acid Perceptual distortion (visual, auditory),
diethylamide depersonalization, anxiety, paranoia,
psychosis, flashbacks (usually nondisturbing).
Marijuana Euphoria, anxiety, paranoid delusions, Irritability, anxiety, depression, insomnia,
(cannabinoid) perception of slowed time, impaired judgment, restlessness, appetite.
social withdrawal, appetite, dry mouth,
conjunctival injection, hallucinations.
Pharmaceutical form is dronabinol: used
as antiemetic (chemotherapy) and appetite
stimulant (in AIDS).
MDMA (ecstasy) Hallucinogenic stimulant: euphoria, Depression, fatigue, change in appetite,
hallucinations, disinhibition, hyperactivity, difficulty concentrating, anxiety.
thirst, bruxism, distorted sensory and time
perception. Life-threatening effects include
hypertension, tachycardia, hyperthermia,
hyponatremia, serotonin syndrome.
Phencyclidine Violence, impulsivity, psychomotor agitation,
nystagmus, tachycardia, hypertension,
analgesia, psychosis, delirium, seizures.
Trauma is most common complication.
Alcohol use disorder Physiologic tolerance and dependence on alcohol with symptoms of withdrawal when intake is
interrupted.
Complications: vitamin B (thiamine) deficiency, alcoholic cirrhosis, hepatitis, pancreatitis,
1
peripheral neuropathy, testicular atrophy.
Treatment: naltrexone (reduces cravings), acamprosate, disulfiram (to condition the patient to
abstain from alcohol use). Support groups such as Alcoholics Anonymous are helpful in sustaining
abstinence and supporting patient and family.
Wernicke-Korsakoff Results from vitamin B deficiency. Symptoms can be precipitated by administering dextrose
1
syndrome before vitamin B . Triad of confusion, ophthalmoplegia, ataxia (Wernicke encephalopathy). May
1
progress to irreversible memory loss, confabulation, personality change (Korsakoff syndrome).
Treatment: IV vitamin B (before dextrose).
1
FAS1_2019_13-Psych.indd 571 11/7/19 5:28 PM