Page 657 - The City and Guilds Textbook: Plumbing Book 1 for the Level 3 Apprenticeship (9189), Level 2 Technical Certificate (8202) and Level 2 Diploma (6035)
P. 657
Chapter 11 Electrical principles and processes for building services engineering
In a DC circuit the direction of conventional current never reverses. Direct
current can be produced from a number of sources, including electrochemical
batteries or photovoltaic cells.
Alternating current
KEY TERM
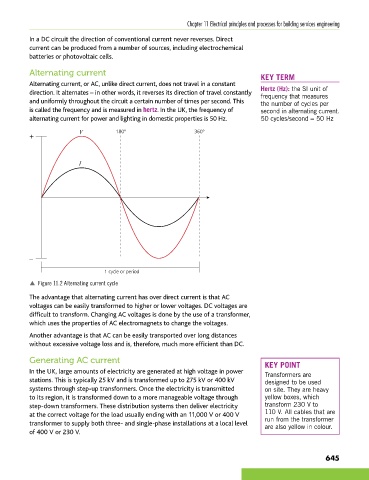
Alternating current, or AC, unlike direct current, does not travel in a constant
direction. It alternates – in other words, it reverses its direction of travel constantly Hertz (Hz): the SI unit of
frequency that measures
and uniformly throughout the circuit a certain number of times per second. This the number of cycles per
is called the frequency and is measured in hertz. In the UK, the frequency of second in alternating current.
alternating current for power and lighting in domestic properties is 50 Hz. 50 cycles/second = 50 Hz
V 180° 360°
+
I
_
1 cycle or period
p Figure 11.2 Alternating current cycle
The advantage that alternating current has over direct current is that AC
voltages can be easily transformed to higher or lower voltages. DC voltages are
difficult to transform. Changing AC voltages is done by the use of a transformer,
which uses the properties of AC electromagnets to change the voltages.
Another advantage is that AC can be easily transported over long distances
without excessive voltage loss and is, therefore, much more efficient than DC.
Generating AC current
KEY POINT
In the UK, large amounts of electricity are generated at high voltage in power Transformers are
stations. This is typically 25 kV and is transformed up to 275 kV or 400 kV designed to be used
systems through step-up transformers. Once the electricity is transmitted on site. They are heavy
to its region, it is transformed down to a more manageable voltage through yellow boxes, which
step-down transformers. These distribution systems then deliver electricity transform 230 V to
at the correct voltage for the load usually ending with an 11,000 V or 400 V 110 V. All cables that are
transformer to supply both three- and single-phase installations at a local level run from the transformer
are also yellow in colour.
of 400 V or 230 V.
645
9781510416482.indb 645 29/03/19 9:09 PM