Page 27 - Module DMV20173
P. 27
2.0 CASTING PROCESSES
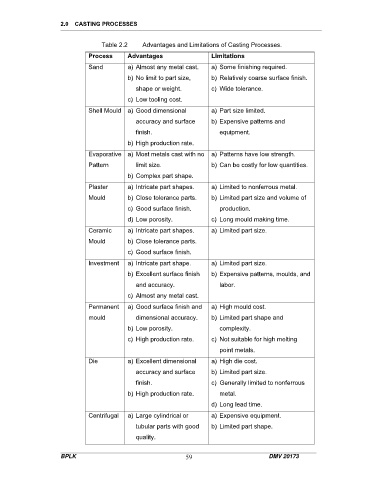
Table 2.2 Advantages and Limitations of Casting Processes.
Process Advantages Limitations
Sand a) Almost any metal cast. a) Some finishing required.
b) No limit to part size, b) Relatively coarse surface finish.
shape or weight. c) Wide tolerance.
c) Low tooling cost.
Shell Mould a) Good dimensional a) Part size limited.
accuracy and surface b) Expensive patterns and
finish. equipment.
b) High production rate.
Evaporative a) Most metals cast with no a) Patterns have low strength.
Pattern limit size. b) Can be costly for low quantities.
b) Complex part shape.
Plaster a) Intricate part shapes. a) Limited to nonferrous metal.
Mould b) Close tolerance parts. b) Limited part size and volume of
c) Good surface finish. production.
d) Low porosity. c) Long mould making time.
Ceramic a) Intricate part shapes. a) Limited part size.
Mould b) Close tolerance parts.
c) Good surface finish.
Investment a) Intricate part shape. a) Limited part size.
b) Excellent surface finish b) Expensive patterns, moulds, and
and accuracy. labor.
c) Almost any metal cast.
Permanent a) Good surface finish and a) High mould cost.
mould dimensional accuracy. b) Limited part shape and
b) Low porosity. complexity.
c) High production rate. c) Not suitable for high melting
point metals.
Die a) Excellent dimensional a) High die cost.
accuracy and surface b) Limited part size.
finish. c) Generally limited to nonferrous
b) High production rate. metal.
d) Long lead time.
Centrifugal a) Large cylindrical or a) Expensive equipment.
tubular parts with good b) Limited part shape.
quality.
BPLK 59 DMV 20173