Page 19 - Grab Me SPM Add Mathematics Form 4,5
P. 19
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
Trigonometry
CHAPTER 6 TRIGONOMETRIC FUNCTIONS
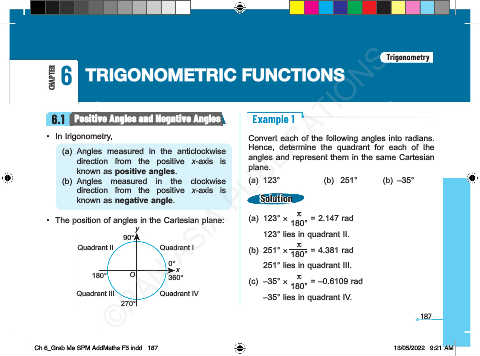
6.1 Positive Angles and Negative Angles Example 1
• In trigonometry, Convert each of the following angles into radians.
(a) Angles measured in the anticlockwise Hence, determine the quadrant for each of the
direction from the positive x-axis is angles and represent them in the same Cartesian
known as positive angles. plane.
(b) Angles measured in the clockwise (a) 123° (b) 251° (b) –35°
direction from the positive x-axis is
known as negative angle. Solution
p
• The position of angles in the Cartesian plane: (a) 123° × 180° = 2.147 rad
y 123° lies in quadrant II.
90°
p
Quadrant II Quadrant I (b) 251° × 180° = 4.381 rad
0° 251° lies in quadrant III.
x
180° O 360° (c) –35° × p = –0.6109 rad
180°
Quadrant III Quadrant IV –35° lies in quadrant IV.
270°
187
Ch 6_Grab Me SPM AddMaths F5.indd 187 13/05/2022 9:21 AM