Page 11 - Spotlight A+ SPM Additional Mathematics Form 4 & 5
P. 11
Form
4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 2 Quadratic Functions
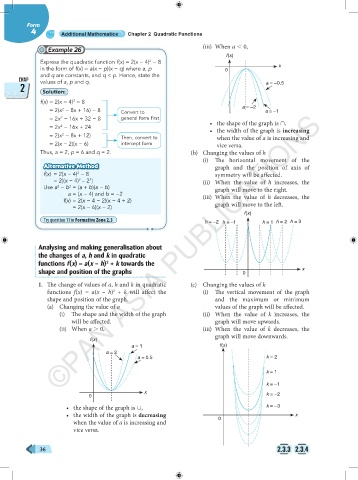
Example 26 (iii) When a 0,
f(x)
Express the quadratic function f(x) = 2(x − 4) − 8
2
in the form of f(x) = a(x − p)(x − q) where a, p 0 x
and q are constants, and q < p. Hence, state the
CHAP values of a, p and q. a = –0.5
2 Solution:
f(x) = 2(x − 4) − 8
2
= 2(x − 8x + 16) − 8 Convert to a = –2 a = –1
2
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
= 2x − 16x + 32 − 8 general form first • the shape of the graph is ∩,
2
2
= 2x − 16x + 24
• the width of the graph is increasing
= 2(x − 8x + 12) Then, convert to when the value of a is increasing and
2
= 2(x − 2)(x − 6) intercept form vice versa.
Thus, a = 2, p = 6 and q = 2. (b) Changing the values of h
(i) The horizontal movement of the
Al te rnative Me thod graph and the position of axis of
Alternative Method
f(x) = 2(x − 4) − 8 symmetry will be affected.
2
= 2[(x − 4) – 2 ] (ii) When the value of h increases, the
2
2
2
2
Use a − b = (a + b)(a − b) graph will move to the right.
a = (x − 4) and b = −2 (iii) When the value of h decreases, the
f(x) = 2(x − 4 − 2)(x − 4 + 2)
= 2(x − 6)(x − 2) graph will move to the left.
f(x)
Try question 11 in Formative Zone 2.3
h = –2 h = –1 h = 1 h = 2 h = 3
Analysing and making generalisation about
the changes of a, h and k in quadratic
2
functions f (x) = a(x – h) + k towards the
shape and position of the graphs 0 x
1. The change of values of a, h and k in quadratic (c) Changing the values of k
functions f(x) = a(x – h) + k will affect the (i) The vertical movement of the graph
2
shape and position of the graph. and the maximum or minimum
(a) Changing the value of a values of the graph will be affected.
(i) The shape and the width of the graph (ii) When the value of k increases, the
will be affected. graph will move upwards.
(ii) When a 0, (iii) When the value of k decreases, the
graph will move downwards.
f(x)
a = 1 f(x)
a = 2
a = 0.5 k = 2
k = 1
k = –1
x
0 k = –2
• the shape of the graph is ∪, k = –3
• the width of the graph is decreasing x
when the value of a is increasing and 0
vice versa.
36 2.3.3 2.3.4