Page 8 - Spotlight A+ SPM Additional Mathematics Form 4 & 5
P. 8
Form
4 Additional Mathematics Chapter 1 Functions
CHAP
1
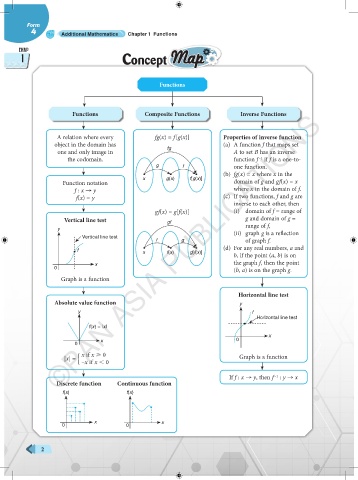
Functions
Functions Composite Functions Inverse Functions
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
A relation where every fg(x) = f [g(x)] Properties of inverse function
object in the domain has (a) A function f that maps set
one and only image in fg A to set B has an inverse
the codomain. function f if f is a one-to-
–1
g f one function.
(b) fg(x) = x where x in the
x g(x) f[g(x)]
Function notation domain of g and gf(x) = x
f : x → y where x in the domain of f.
f(x) = y (c) If two functions, f and g are
inverse to each other, then
gf(x) = g[f(x)] (i) domain of f = range of
Vertical line test gf g and domain of g =
y range of f,
(ii) graph g is a reflection
Vertical line test
f g of graph f.
(d) For any real numbers, a and
f
x f(x) g[f(x)]
b, if the point (a, b) is on
the graph f, then the point
x
0 (b, a) is on the graph g.
Graph is a function
Horizontal line test
Absolute value function y
y f
Horizontal line test
f(x) = |x|
x
x 0
0
x if x 0
|x| = –x if x 0 Graph is a function
If f : x → y, then f : y → x
–1
Discrete function Continuous function
f(x) f(x)
x x
0 0
2