Page 31 - Spotlight A+ SPM Additional Mathematics Form 4 & 5
P. 31
Form
5 Additional Mathematics Chapter 2 Differentiation
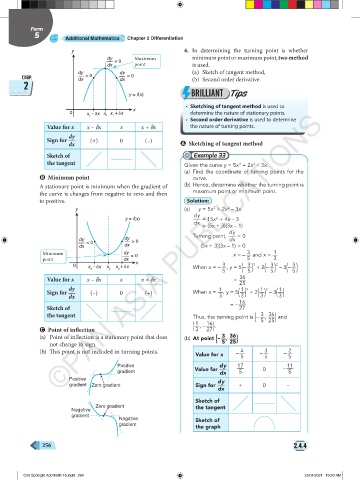
y 6. In determining the turning point is whether
dy Maximum minimum point or maximum point, two method
— = 0
dx point is used.
dy dy (a) Sketch of tangent method,
CHAP. — > 0 — < 0 (b) Second order derivative.
dx
dx
2
y = f(x) BRILLIANT Tips
• Sketching of tangent method is used to
x
0 x – x x x + x determine the nature of stationary points.
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
1 1 1
• Second order derivative is used to determine
Value for x x – dx x x + dx the nature of turning points.
dy
Sign for (+) 0 (–)
dx A Sketching of tangent method
Sketch of Example 33
the tangent Given the curve y = 5x + 2x – 3x.
3
2
(a) Find the coordinate of turning points for the
B Minimum point curve.
A stationary point is minimum when the gradient of (b) Hence, determine whether the turning point is
the curve is changes from negative to zero and then maximum point or minimum point.
to positive. Solution:
2
3
y (a) y = 5x + 2x – 3x
dy
2
y = f(x) = 15x + 4x – 3
dx = (5x + 3)(3x – 1)
dy
Turning point, = 0
dy dy dx
— < 0 — > 0
dx dx (5x + 3)(3x – 1) = 0
3
dy
Minimum — = 0 x = – and x = 1
point dx 5 3
( ) ( )
( )
x
3
0 x – x x x + x When x = – , y = 5 – 3 3 + 2 – 3 2 – 3 – 3
2 2 2 5 5 5 5
Value for x x – dx x x + dx = 36
25
dy 1 1
1 2
1 3
Sign for (–) 0 (+) When x = , y = 5 ( ) + 2 ( ) ( )
– 3
dx 3 3 3 3
= – 16
Sketch of 27
(
3 36
the tangent Thus, the turning point is – , ) and
( 1 , – 16 ) . 5 25
C Point of inflection 3 27
3 36
(a) Point of inflection is a stationary point that does (b) At point – , )
(
not change in sign. 5 25
(b) This point is not included in turning points. – 4 – 3 – 2
Value for x 5 5 5
Positive dy 17 0 – 11
gradient Value for dx 5 5
Positive dy
gradient Zero gradient Sign for + 0 –
dx
Sketch of
Zero gradient
Negative the tangent
gradient
Negative Sketch of
gradient
the graph
256 2.4.4
C02 Spotlight Add Math F5.indd 256 23/04/2021 10:53 AM