Page 25 - Spotlight A+ Physics Form 4.5
P. 25
Form
5 Physics Chapter 7 Quantum Physics
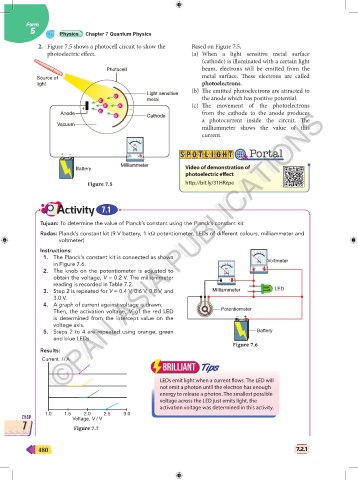
2. Figure 7.5 shows a photocell circuit to show the Based on Figure 7.5,
photoelectric effect. (a) When a light sensitive metal surface
(cathode) is illuminated with a certain light
Photocell beam, electrons will be emitted from the
metal surface. These electrons are called
Source of
light photoelectrons.
(b) The emitted photoelectrons are attracted to
Light sensitive
e - the anode which has positive potential.
e - metal
e - e - (c) The movement of the photoelectrons
+ - _
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
Anode e from the cathode to the anode produces
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
e - Cathode
a photocurrent inside the circuit. The
Vacuum
milliammeter shows the value of this
current.
2 3
1 4
0 5
mA
+ _
− +
Milliammeter Video of demonstration of
Battery
photoelectric effect
Figure 7.5 http://bit.ly/31HRcpe
Activity 7.1
Tujuan: To determine the value of Planck’s constant using the Planck’s constant kit
Radas: Planck’s constant kit (9 V battery, 1 kΩ potentiometer, LEDs of different colours, milliammeter and
voltmeter)
Instructions: 2 3
1 0 4 5
1. The Planck's constant kit is connected as shown V
Voltmeter
in Figure 7.6. 1 2 3 4
0 5
2. The knob on the potentiometer is adjusted to mA − +
obtain the voltage, V = 0.2 V. The milliammeter
− +
reading is recorded in Table 7.2.
3. Step 2 is repeated for V = 0.4 V, 0.6 V, 0.8 V, and Milliammeter LED
3.0 V.
4. A graph of current against voltage is drawn.
Then, the activation voltage, V of the red LED Potentiometer
a – +
is determined from the intercept value on the
voltage axis.
5. Steps 2 to 4 are repeated using orange, green Battery
and blue LEDs.
Figure 7.6
Results:
Current, I / A
LEDs emit light when a current flows. The LED will
not emit a photon until the electron has enough
energy to release a photon. The smallest possible
voltage across the LED just emits light, the
activation voltage was determined in this activity.
1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0
CHAP Voltage, V / V
7 Figure 7.7
480 7.2.1