Page 19 - 1202 Question Bank Physics Form 5
P. 19
(e) h r = h r • Mass is equal to the product of density and volume.
1 1 2 2
900 µ 1.2 = r µ 0.85 • Since the density of the oil is less, the volume to be
Y
r = 1.27 µ 10 kg m –3 displaced must be more. So, the wooden cube sinks more
3
Y
6. (a) (i) Vacuum (Torricelli) to do so.
(ii) Same
(b) h r = h r Paper 3
1 1 2 2
0.760 µ 13.6 = h µ 1
2
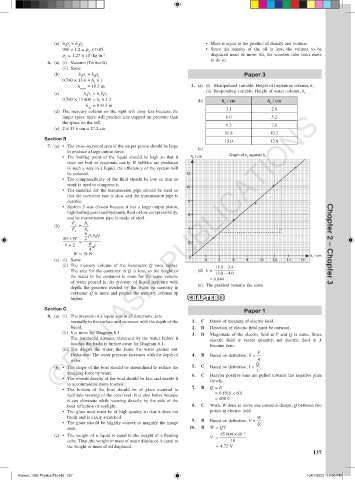
h = 10.3 m 1. (a) (i) Manipulated variable: Height of turpentine column, h
water 1
(c) h r = h Vr (ii) Responding variable: Height of water column, h 2
1 1 2 2
0.760 µ 13 600 = h µ 1.2
2 (b) h / cm h / cm
2
1
h = 8 613 m
air 3.1 2.6
(d) The mercury column on the right will drop less because the
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
larger space there will produce less trapped air pressure than 6.0 5.2
the space on the left.
9.2 7.6
(e) 2 µ 13.6 cm = 27.2 cm
11.8 10.2
Section B
15.0 12.8
7. (a) • The cross-sectional area of the output piston should be large (c)
to produce a large output force.
• The boiling point of the liquid should be high so that it h / cm Graph of h against h 1
2
2
does not boil or evaporate easily. If bubbles are produced
in such a way in a liquid, the efficiency of the system will
be reduced. 12
• The compressibility of the fluid should be low so that no
work is used to compress it.
10
• The material for the transmission pipe should be steel so
that the corrosion rate is slow and the transmission pipe is
durable. 8
• System S was chosen because it has a large output piston,
high boiling point and hydraulic fluid of low compressibility,
6
and its transmission pipe is made of steel.
F A
(b) 1 = 1
F A 4
2 2
p 2
80 + W 4 (3.5d)
= p 2
6 + 2 d 2 Chapter 2 – Chapter 3
4
W = 18 N
0 h / cm
1
(c) (i) Same 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16
(ii) The mercury column of the barometer Q rises higher. 11.0 – 3.4
The area for the container in Q is less, so the height of (d) k = 13.0 – 4.0
the water in the container is more for the same volume = 0.844
of water poured in. As pressure of liquid increases with
depth, the pressure exerted by the water on mercury in (e) The gradient remains the same
container Q is more and pushes the mercury column up
higher. CHAPTER 3
Section C
Paper 1
8. (a) (i) The pressure of a liquid acts in all directions, acts
normally to the surface and increases with the depth of the 1. C Based of meaning of electric field.
liquid. 2. D Direction of electric field must be outward.
(ii) h is more for Diagram 8.1. 3. D Magnitude of the electric field at P and Q is same. Since
The horizontal distance traversed by the water before it electric field is vector quantity, net electric field at X
touches the basin is further away for Diagram 8.1. become zero.
(iii) The deeper the water, the faster the water gushes out. F
Deduction: The water pressure increases with the depth of 4. B Based on definition, E = .
water. Q q
(b) • The shape of the boat should be streamlined to reduce the 5. C Based on definition, I = .
t
dragging force by water. 6. C Heavier positive ions are pulled towards the negative plate
• The overall density of the boat should be less and enable it slowly.
to accommodate more tourists.
• The bottom of the boat should be of glass material to 7. B Q = It
facilitate viewing of the coral reef. It is also better because = 0.85(8 × 60)
it can eliminate while viewing directly by the side of the = 408 C
boat reflection of sunlight. 8. C Work, W done to move one coulomb charge, Q between two
• The glass used must be of high quality so that it does not points in electric field.
break and is easily scratched. W
• The glass should be slightly convex to magnify the image 9. B Based on definition, V = .
Q
seen. 10. B W = QV
(c) • The weight of a liquid is equal to the weight of a floating V = 85 000 × 10 –3
cube. Thus, the weight or mass of water displaced is equal to 18
the weight or mass of oil displaced. = 4.72 V
137
Answer_1202 Physics F5.indd 137 10/01/2022 12:50 PM