Page 4 - 1202 Question Bank Mathematics Form 5
P. 4
MUST
KNOW Important Facts
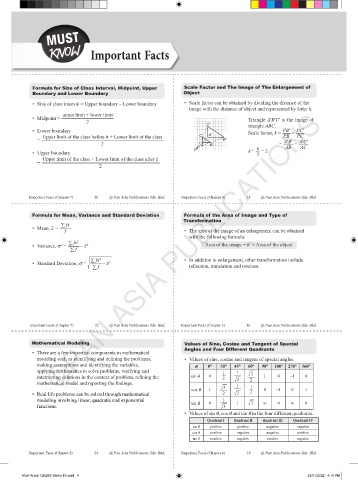
Formula for Size of Class Interval, Midpoint, Upper Scale Factor and The Image of The Enlargement of
Boundary and Lower Boundary Object
• Size of class interval = Upper boundary – Lower boundary • Scale factor can be obtained by dividing the distance of the
image with the distance of object and represented by letter k.
upper limit + lower limit
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
• Midpoint = Triangle A′B′C′ is the image of
2
C' triangle ABC.
• Lower boundary Scale factor, k = PB′ = PC′
Upper limit of the class before it + Lower limit of the class C A' PB PC
= B' A′B′ A′C′
2 A B = AB = AC
6
• Upper boundary P k = = 2
3
Upper limit of the class + Lower limit of the class after it
=
2
Important Facts (Chapter 7) 20 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd. Important Facts (Chapter 5) 14 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd.
Formula for Mean, Variance and Standard Deviation Formula of the Area of Image and Type of
Transformation
–
• Mean, x = ∑ fx
f • The area of the image of an enlargement can be obtained
with the following formula:
∑ fx 2
2
• Variance, s = – x –2 Area of the image = k × Area of the object
2
∑ f
!
• Standard Deviation, s = ∑ fx 2 – x –2 • In addition to enlargement, other transformation include
reflection, translation and rotation.
∑ f
Important Facts (Chapter 7) 22 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd. Important Facts (Chapter 5) 16 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd.
Mathematical Modeling Values of Sine, Cosine and Tangent of Special
Angles and Four Different Quadrants
• There are a few important components in mathematical
modeling such as identifying and defining the problems, • Values of sine, cosine and tangent of special angles.
making assumptions and identifying the variables, q 0° 30° 45° 60° 90° 180° 270° 360°
applying mathematics to solve problems, verifying and 1 1
interpreting solutions in the context of problem, refining the sin q 0 2 ! 2 ! 3 1 0 –1 0
2
mathematical model and reporting the findings. 1
cos q 1 ! 3 1 0 –1 0 1
• Real-life problems can be solved through mathematical 2 ! 2 2
modeling involving linear, quadratic and exponential 0 1 1 ! 3 ∞ 0 ∞ 0
functions. tan q ! 3
• Values of sin q, cos q and tan q in the four different quadrants.
Quadrant I Quadrant II Quadrant III Quadrant IV
sin q positive positive negative negative
cos q positive negative negative positive
tan q positive negative positive negative
Important Facts (Chapter 8) 24 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd. Important Facts (Chapter 6) 18 @ Pan Asia Publications Sdn. Bhd.
Must Know 1202BS Maths F5.indd 4 21/01/2022 4:16 PM