Page 7 - 1202 Question Bank Mathematics Form 5
P. 7
Chapter 1 Variation
NOTes
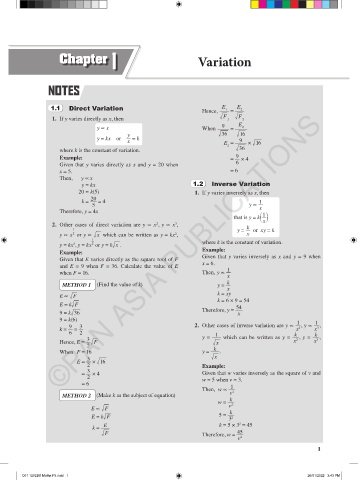
1.1 Direct Variation Hence, E 1 = E 2
©PAN ASIA PUBLICATIONS
1. If y varies directly as x, then ! F 1 ! F 2
y fi x When 9 = E 2
y ! 36 ! 16
y = kx or = k
x E = 9 × ! 16
2
where k is the constant of variation. ! 36
Example: = 9 × 4
Given that y varies directly as x and y = 20 when 6
x = 5. = 6
Then, y fi x
y = kx 1.2 Inverse Variation
20 = k(5) 1. If y varies inversely as x, then
20
k = = 4 1
5 y fi x
Therefore, y = 4x
1
that is y = k ( )
x
2
3
2. Other cases of direct variation are y fi x , y fi x ,
k
1 y = or xy = k
2
2
y fi x or y fi ! x which can be written as y = kx , x
1
3
2
y = kx , y = kx or y = k! x . where k is the constant of variation.
Example:
Example:
Given that E varies directly as the square root of F Given that y varies inversely as x and y = 9 when
and E = 9 when F = 36. Calculate the value of E x = 6. 1
when F = 16. Then, y fi
x
METHOD 1 (Find the value of k) y = k
x
k = xy
E fi ! F
k = 6 × 9 = 54
E = k! F 54
Therefore, y =
9 = k! 36 x
9 = k(6) 1 1
9 3 2. Other cases of inverse variation are y fi , y fi ,
3
2
k = = x x
6 2 1 k k
3 y = which can be written as y = x 2 , y = x 3 ,
Hence, E = ! F ! x
2
When F = 16 y = k .
! x
3
E = × ! 16
2 Example:
3
= × 4 Given that w varies inversely as the square of v and
2 w = 5 when v = 3.
= 6
Then, w fi 1 2
METHOD 2 (Make k as the subject of equation) v
w = k 2
E fi ! F v k
E = k! F 5 = 3 2
2
E k = 5 × 3 = 45
k =
! F Therefore, w = 45
v 2
1
C01 1202BS Maths F5.indd 1 26/01/2022 3:43 PM