Page 507 - (ISC)² CISSP Certified Information Systems Security Professional Official Study Guide
P. 507
The Clark-Wilson model does not require the use of a lattice structure;
rather, it uses a three-part relationship of subject/program/object (or
subject/transaction/object) known as a triple or an access control
triple. Subjects do not have direct access to objects. Objects can be
accessed only through programs. Through the use of two principles—
well-formed transactions and separation of duties—the Clark-Wilson
model provides an effective means to protect integrity.
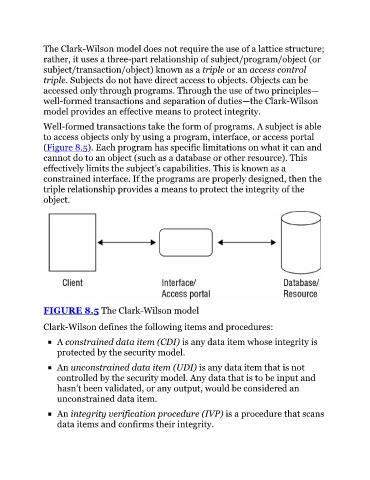
Well-formed transactions take the form of programs. A subject is able
to access objects only by using a program, interface, or access portal
(Figure 8.5). Each program has specific limitations on what it can and
cannot do to an object (such as a database or other resource). This
effectively limits the subject’s capabilities. This is known as a
constrained interface. If the programs are properly designed, then the
triple relationship provides a means to protect the integrity of the
object.
FIGURE 8.5 The Clark-Wilson model
Clark-Wilson defines the following items and procedures:
A constrained data item (CDI) is any data item whose integrity is
protected by the security model.
An unconstrained data item (UDI) is any data item that is not
controlled by the security model. Any data that is to be input and
hasn’t been validated, or any output, would be considered an
unconstrained data item.
An integrity verification procedure (IVP) is a procedure that scans
data items and confirms their integrity.