Page 107 - Elementary_Linear_Algebra_with_Applications_Anton__9_edition
P. 107
1.7 In this section we shall consider certain classes of matrices that have special
forms. The matrices that we study in this section are among the most
DIAGONAL, important kinds of matrices encountered in linear algebra and will arise in
TRIANGULAR, AND many different settings throughout the text.
SYMMETRIC MATRICES
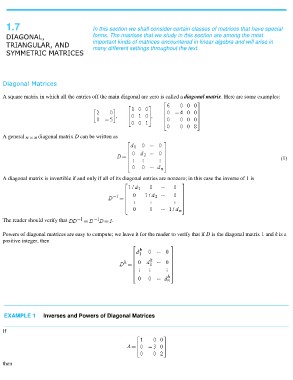
Diagonal Matrices
A square matrix in which all the entries off the main diagonal are zero is called a diagonal matrix. Here are some examples:
A general diagonal matrix D can be written as (1)
A diagonal matrix is invertible if and only if all of its diagonal entries are nonzero; in this case the inverse of 1 is
The reader should verify that .
Powers of diagonal matrices are easy to compute; we leave it for the reader to verify that if D is the diagonal matrix 1 and k is a
positive integer, then
EXAMPLE 1 Inverses and Powers of Diagonal Matrices
If
then