Page 831 - Elementary_Linear_Algebra_with_Applications_Anton__9_edition
P. 831
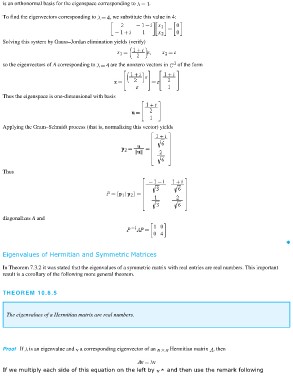
is an orthonormal basis for the eigenspace corresponding to .
To find the eigenvectors corresponding to , we substitute this value in 4:
Solving this system by Gauss–Jordan elimination yields (verify)
so the eigenvectors of A corresponding to are the nonzero vectors in of the form
Thus the eigenspace is one-dimensional with basis
Applying the Gram–Schmidt process (that is, normalizing this vector) yields
Thus
diagonalizes A and
Eigenvalues of Hermitian and Symmetric Matrices
In Theorem 7.3.2 it was stated that the eigenvalues of a symmetric matrix with real entries are real numbers. This important
result is a corollary of the following more general theorem.
THEOREM 10.6.5
The eigenvalues of a Hermitian matrix are real numbers.
Proof If is an eigenvalue and a corresponding eigenvector of an Hermitian matrix , then
If we multiply each side of this equation on the left by and then use the remark following