Page 37 - Lecture Notes DCC3113
P. 37
Table 3-1: Different between Asphalt vs Bitumen
Asphalt Bitumen
American European
Thailand Malaysia
Asphalt / Asphalt Cement (AC) Bitumen
Hot Mix = AC + Aggregate Premix = Bitumen + Aggregate
Hot Mix Asphalt (HMA) / Asphaltic Concrete / Asphalt Concrete
Asphalt Concrete
The objectives of asphaltic mix
The objectives of asphaltic concrete mix design are to produce an asphaltic concrete mix by
proportionating various components so as to have:
• Sufficient asphalt to ensure a durable pavement
• Sufficient stability under traffic loads
• Sufficient air voids
– Upper limit to prevent excessive environmental damage
– Lower limit to allow room for initial densification due to traffic
• Sufficient workability
Characteristics of asphaltic concrete mix
When a sample of asphalt mixture is prepared in the laboratory, the asphalt mixture is analyzed to
determine the probable performance in a pavement structure. The analysis focuses on five
characteristics of the asphalt mixture and the influence those characteristics are likely to have on
asphalt mixture behavior. An asphalt concrete mixture must be designed, produced and placed in
order to obtain the following desirable mix properties:
i. Stability - is its ability to resist shoving and rutting under loads (traffic).
i. Durability - it is the resistance against abrasion and weathering.
ii. Impermeability - Impermeability is the resistance of an asphalt pavement to the passage of air
and water into or through it.
iii. Workability – it is measure of ease with which a bituminous mix can be laid and compacted.
This property is a function of the aggregate grading, shape of particles, texture of particles, type
of bitumen used, and bitumen content.
iv. Flexibility – this property of the mix measures the capability of the surface in bending, without
shearing and cracking.
v. Fatigue Resistance - is the pavement’s resistance to repeated bending under wheel loads (traffic).
vi. Skid Resistance - Skid resistance is the ability of an asphalt surface to minimize skidding or
slipping of vehicle tires, particularly when wet.
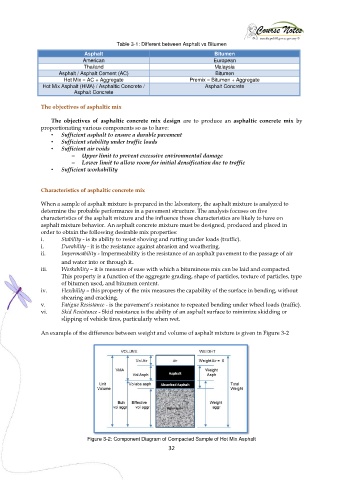
An example of the difference between weight and volume of asphalt mixture is given in Figure 3-2
Figure 3-2: Component Diagram of Compacted Sample of Hot Mix Asphalt
32