Page 39 - Lecture Notes DCC3113
P. 39
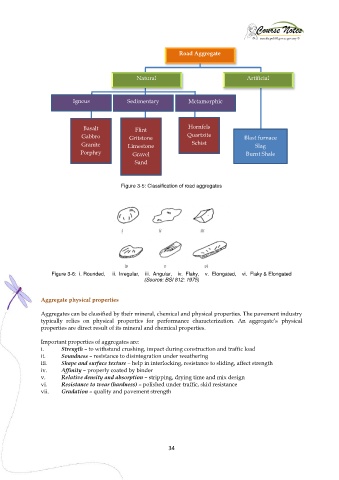
Road Aggregate
Natural Artificial
Igneus Sedimentary Metamorphic
Basalt Flint Hornfels
Gabbro Gritstone Quartzite Blast furnace
Granite Limestone Schist Slag
Porphry Gravel Burnt Shale
Sand
Figure 3-5: Classification of road aggregates
Figure 3-6: i. Rounded, ii. Irregular, iii. Angular, iv. Flaky, v. Elongated, vi. Flaky & Elongated
(Source: BSI 812: 1975)
Aggregate physical properties
Aggregates can be classified by their mineral, chemical and physical properties. The pavement industry
typically relies on physical properties for performance characterization. An aggregate’s physical
properties are direct result of its mineral and chemical properties.
Important properties of aggregates are:
i. Strength – to withstand crushing, impact during construction and traffic load
ii. Soundness – resistance to disintegration under weathering
iii. Shape and surface texture – help in interlocking, resistance to sliding, affect strength
iv. Affinity – properly coated by binder
v. Relative density and absorption – stripping, drying time and mix design
vi. Resistance to wear (hardness) – polished under traffic, skid resistance
vii. Gradation – quality and pavement strength
34