Page 96 - C:\Users\trainee\AppData\Local\Temp\msoEAA3.tmp
P. 96
Document Title
Fundamentals of Stress and Vibration Chapter Title
[A Practical guide for aspiring Designers / Analysts] 2. Engineering Mechanics
Let us find the reactions at the supports by taking moments about the bearing support 1.
L d Mg
R ∗ L = Mg + + mg L + d = R ∗ L = L + d + mg L + d
2
2 2 2 2
Mg d Mg
= R ∗ L = L + d + mg = R = 1 + + mg - - - - (2.69)
2
2 2 L 2
From vertical force balance we have:
d Mg
R = Mg + mg − R = R = Mg + mg − 1 + + mg - - - - (2.70)
1
1
2
L 2
Since the disc-shaft system is spinning and precessing, it experiences a torque about the ‘z-axis’,
called the gyroscopic torque and is given by:
Gyroscopic torque = ω j × Ω i I = ωΩI −k
Since gyroscopic moment is an inertial moment, the reactive moment is considered, which is:
Gyroscopic torque = ωΩI k - - - - (2.71)
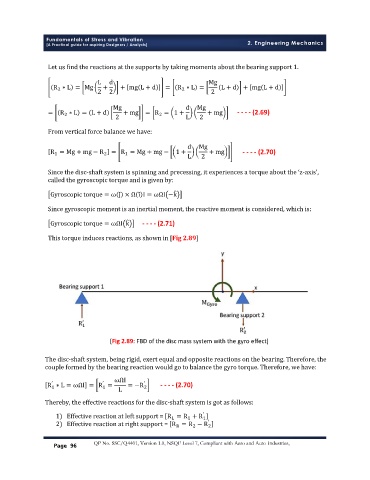
This torque induces reactions, as shown in [Fig 2.89]
[Fig 2.89: FBD of the disc mass system with the gyro effect]
The disc-shaft system, being rigid, exert equal and opposite reactions on the bearing. Therefore, the
couple formed by the bearing reaction would go to balance the gyro torque. Therefore, we have:
ωΩI
′
′
′
R ∗ L = ωΩI = R = = −R - - - - (2.70)
1
2
1
L
Thereby, the effective reactions for the disc-shaft system is got as follows:
1) Effective reaction at left support = R = R + R
′
1
1
L
′
2) Effective reaction at right support = R = R − R
2
R
2
Page 96 QP No. SSC/Q4401, Version 1.0, NSQF Level 7, Compliant with Aero and Auto Industries,