Page 108 - Fisika Terapan for Engineers and Scientists
P. 108
308 CHAPTER 10 Systems of Particles
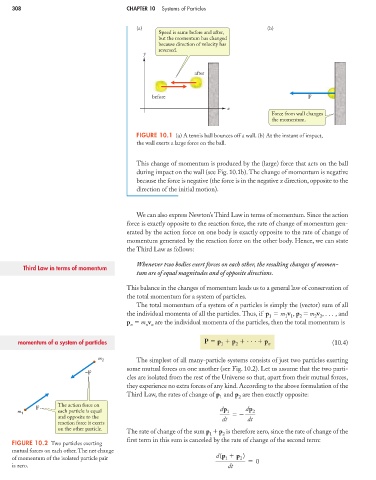
(a) (b)
Speed is same before and after,
but the momentum has changed
because direction of velocity has
reversed.
y
after
before F
x
Force from wall changes
the momentum.
FIGURE 10.1 (a) A tennis ball bounces off a wall. (b) At the instant of impact,
the wall exerts a large force on the ball.
This change of momentum is produced by the (large) force that acts on the ball
during impact on the wall (see Fig. 10.1b).The change of momentum is negative
because the force is negative (the force is in the negative x direction, opposite to the
direction of the initial motion).
We can also express Newton’s Third Law in terms of momentum. Since the action
force is exactly opposite to the reaction force, the rate of change of momentum gen-
erated by the action force on one body is exactly opposite to the rate of change of
momentum generated by the reaction force on the other body. Hence, we can state
the Third Law as follows:
Whenever two bodies exert forces on each other, the resulting changes of momen-
Third Law in terms of momentum
tum are of equal magnitudes and of opposite directions.
This balance in the changes of momentum leads us to a general law of conservation of
the total momentum for a system of particles.
The total momentum of a system of n particles is simply the (vector) sum of all
the individual momenta of all the particles. Thus, if p m v , p m v , ..., and
1 1 1 2 2 2
p m v are the individual momenta of the particles, then the total momentum is
n n n
momentum of a system of particles P p p p n (10.4)
2
1
m 2 The simplest of all many-particle systems consists of just two particles exerting
some mutual forces on one another (see Fig. 10.2). Let us assume that the two parti-
–F
cles are isolated from the rest of the Universe so that, apart from their mutual forces,
they experience no extra forces of any kind. According to the above formulation of the
Third Law, the rates of change of p and p are then exactly opposite:
1 2
The action force on
F dp dp
m 1 each particle is equal 1 2
and opposite to the dt dt
reaction force it exerts
on the other particle.
The rate of change of the sum p p is therefore zero, since the rate of change of the
1 2
first term in this sum is canceled by the rate of change of the second term:
FIGURE 10.2 Two particles exerting
mutual forces on each other. The net change
d (p p )
of momentum of the isolated particle pair 1 2
0
is zero. dt