Page 203 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 203
Clinical Presentation and Management 179
of Acute Heart Failure
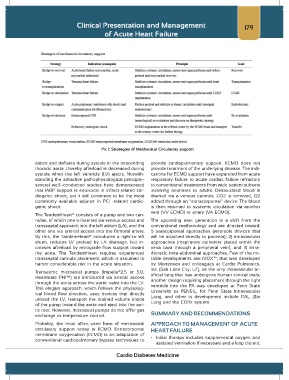
Pic 1: Strategies of Mechanical Circulatory support
astole and deflates during systole in the descending provide cardiopulmonary support. ECMO does not
thoracic aorta ,thereby afterload is decreased during provide treatment of the underlying disease. The indi-
systole when the left ventricle (LV) ejects. Notwith- cations for ECMO support have expanded from acute
standing the attractive pathophysiological principle,- respiratory failure to acute cardiac failure refractory
several well -conducted studies have demonstrated to conventional treatments from wide patient subsets
that IABP support is equivocal in infarct-related car- involving neonates to adults. Desaturated blood is
diogenic shock, yet it still continues to be the most drained via a venous cannula. CO2 is removed, O2
commonly available adjunct in PCI -related cardio- added through an “extracorporeal” device. The blood
genic shock. is then returned to systemic circulation via another
vein (VV ECMO) or artery (VA ECMO).
The TandemHeart® consists of a pump and two can-
nulas, of which one is inserted via venous access and The upcoming next generation is a shift from the
transseptal approach into the left atrium (LA), and the conventional methodology and are directed toward:
other one via arterial access into the femoral artery. 1) paracorporeal approaches (wearable devices that
By this, the TandemHeart® introduces a right-to-left will be attached directly to patients); 2) intravascular
shunt, reduces LV preload by LA drainage, but in- approaches (respiratory catheters placed within the
creases afterload by retrograde flow support toward vena cava through a peripheral vein); and 3) intra-
the aorta. The TandemHeart requires experienced thoracic-intra-abdominal approaches. Few of the no-
transseptal cannula placement, which is assumed to table developments are: iVOX™, that was developed
harbor considerable risk in the acute situation. by Mortensen and colleagues at Cardio Pulmonics,
Inc. (Salt Lake City, UT), as the only intravascular ar-
Transaortic microaxial pumps (Impella®2.5 or 5.0, tificial lung that has undergone human clinical trials;
Heartmate PHP®) are introduced via arterial access another design requiring placement through the right
through the aorta across the aortic valve into the LV. ventricle into the PA was developed at Penn State
This elegant approach, which follows the physiolog- University as PENSIL, for Penn State Intravascular
ical blood flow direction, uses devices that directly Lung, and other in development include ITAL ,Bio
unload the LV, transport the drained volume inside Lung and the CORx system.
of the pump toward the aorta and eject into the aor-
tic root. However, microaxial pumps do not offer gas
exchange or temperature control. SUMMARY AND RECOMMENDATIONS
Probably, the most often used form of mechanical APPROACH TO MANAGEMENT OF ACUTE
circulatory support today is ECMO. Extracorporeal HEART FAILURE
membrane oxygenation (ECMO) is an adaptation of • Initial therapy includes supplemental oxygen and
conventional cardiopulmonary bypass techniques to
assisted ventilation if necessary and a loop diuretic
Cardio Diabetes Medicine