Page 291 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 291
Cardio Diabetes Medicine 2017 267
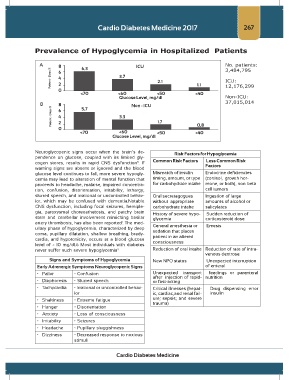
A 8 6.3 ICU
Patient - Days % 6 3.7 2.1
4
2
0 1.1
<70 <60 <50 <40
Glucose Level, mg/dl
B 8 5.7 Non - ICU
Patient - Days % 6 3.3 1.7
4
2
0 0.8
<70 <60 <50 <40
Glucose Level, mg/dl
Neuroglycopenic signs occur when the brain’s de- Risk Factors for Hypoglycemia
pendence on glucose, coupled with its limited gly-
cogen stores, results in rapid CNS dysfunction . If Common Risk Factors Less Common Risk
5
warning signs are absent or ignored and the blood Factors
glucose level continues to fall, more severe hypogly- Mismatch of insulin Endocrine deficiencies
cemia may lead to alteration of mental function that timing, amount, or type (cortisol, growth hor-
proceeds to headache, malaise, impaired concentra- for carbohydrate intake mone, or both), non–beta
tion, confusion, disorientation, irritability, lethargy, cell tumors
slurred speech, and irrational or uncontrolled behav- Oral secretagogues Ingestion of large
ior, which may be confused with dementia.Notable without appropriate amounts of alcohol or
CNS dysfunction, including focal seizures, hemiple- carbohydrate intake salicylates
gia, paroxysmal choreoathetosis, and patchy brain History of severe hypo- Sudden reduction of
stem and cerebellar involvement mimicking basilar glycemia corticosteroid dose
artery thrombosis, has also been reported . The med- General anesthesia or Emesis
1
ullary phase of hypoglycemia, characterized by deep sedation that places
coma, pupillary dilatation, shallow breathing, brady- patient in an altered
cardia, and hypotonicity, occurs at a blood glucose consciousness
level of ~ 10 mg/dl.6 Most individuals with diabetes
never suffer such severe hypoglycemia 4 Reduction of oral intake Reduction of rate of intra-
venous dextrose
Signs and Symptoms of Hypoglycemia New NPO status Unexpected interruption
Early Adrenergic Symptoms Neuroglycopenic Signs of enteral
• Pallor • Confusion Unexpected transport feedings or parenteral
after injection of rapid- nutrition
• Diaphoresis • Slurred speech or fast-acting
• Tachycardia • Irrational or uncontrolled behav- Critical illnesses (hepat- Drug dispensing error
ior ic, cardiac,and renal fail- insulin
• Shakiness • Extreme fatigue ure; sepsis; and severe
trauma)
• Hunger • Disorientation
• Anxiety • Loss of consciousness
• Irritability • Seizures
• Headache • Pupillary sluggishness
• Dizziness • Decreased response to noxious
stimuli
Cardio Diabetes Medicine