Page 294 - fbkCardioDiabetes_2017
P. 294
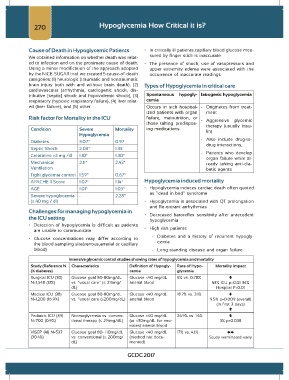
270 Hypoglycemia How Critical it is?
Cause of Death in Hypoglycemic Patients • In critically ill patients,capillary blood glucose mea-
sured by finger stick is inaccurate
We obtained information on whether death was relat-
ed to infection and on the proximate cause of death. • The presence of shock, use of vasopressors and
Using a minor modification of the approach adopted upper extremity edema were associated with the
by the NICE-SUGAR trial. we created 5 cause-of-death occurrence of inaccurate readings
categories: (1) neurologic (traumatic and nontraumatic
brain injury both with and without brain death), (2) Types of Hypoglycemia in critical care
cardiovascular (arrhythmia, cardiogenic shock, dis-
tributive [septic] shock and hypovolemic shock), (3) Spontaneous hypogly- Iatrogenic hypoglycemia
respiratory (hypoxic respiratory failure), (4) liver relat- cemia
ed (liver failure), and (5) other. Occurs in sick hospital- - Originates from treat-
ized patients with organ ment
Risk factor for Mortality in the ICU failure, malnutrition, or - Aggressive glycemic
those taking predispos- therapy (usually insu-
Condition Severe Mortality ing medications lin)
Hypoglycemia
- Also include drug-to-
Diabetes 3.07* 0.97
drug interactions,
Septic Shock 2.03* 1.33
- Patients who develop
Creatinine >3 mg /dl 1.10* 1.30*
organ failure while al-
Mechanical 2.11* 2.43* ready taking anti-dia-
Ventilation betic agents
Tight glycemia control 1.59* 0.67*
APACHE II Score 1.07* 1.14* Hypoglycemia induced mortality
AGE 1.01* 1.03* • Hypoglycemia induces cardiac death often quoted
as “dead in bed” syndrome
Severe hypoglycemia - 2.28*
(≤ 40 mg / dl) • Hypoglycemia is associated with QT prolongation
and Re-entrant arrhythmias
Challenges for managing hypoglycemia in • Decreased baroreflex sensitivity after antecedent
the ICU setting
hypoglycemia
• Detection of hypoglycemia is difficult as patients
are unable to communicate • High risk patients
- Diabetes and a history of recurrent hypogly-
• Glucose concentrations may differ according to
the blood sampling site(venous,arterial or capillary cemia
blood) - Long standing disease and organ failure
Intensive glycemic control studies showing rates of hypoglycemia and mortality
Study (Reference N Characteristics Definition of Hypogly- Rate of Hypo- Mortality Impact
(% diabetes) cemia glycemia
Surgical ICU (30) Glucose goal 80-110mg/dL Glucose <40 mg/dL 5% vs. 0.78%
N=1,548 (13%) vs. “usual care” (≤ 215mg/ arterial blood 43% ICU p=0.01 34%
dL) Hospital P=0.01
Medical ICU (38) Glucose goal 80-110mg/dL Glucose <40 mg/dL 18.7% vs. 3.1%
N=1.200 (16.9%) vs. “usual care (≤200mg/dL) arterial blood 9.5% p=0.009 (overall)
(In first 3 days)
Pediatric ICU (39) Normoglycemia vs. conven- Glucose <40 mg/dL 24.9% vs. 1.4%
N=700 (0.9%) tional therapy (≤ 214mg/dL) (or <30mg/dL for neo- 3% p=0.038
nates) arterial blood
VISEP (41) N=537 Glucose goal 80- 110mg/dL Glucose <40 mg/dL 17% vs. 4.1%
(30.4%) vs. conventional (≤ 200mg/ (method not docu- Study terminated early
dL) mented)
GCDC 2017